Meiosis Comic Strip
PROPHASE I
METAPHASE I
ANAPHASE I
TELOPHASE I
PROPHASE II
METAPHASE II
ANAPHASE II
TELOPHASE II
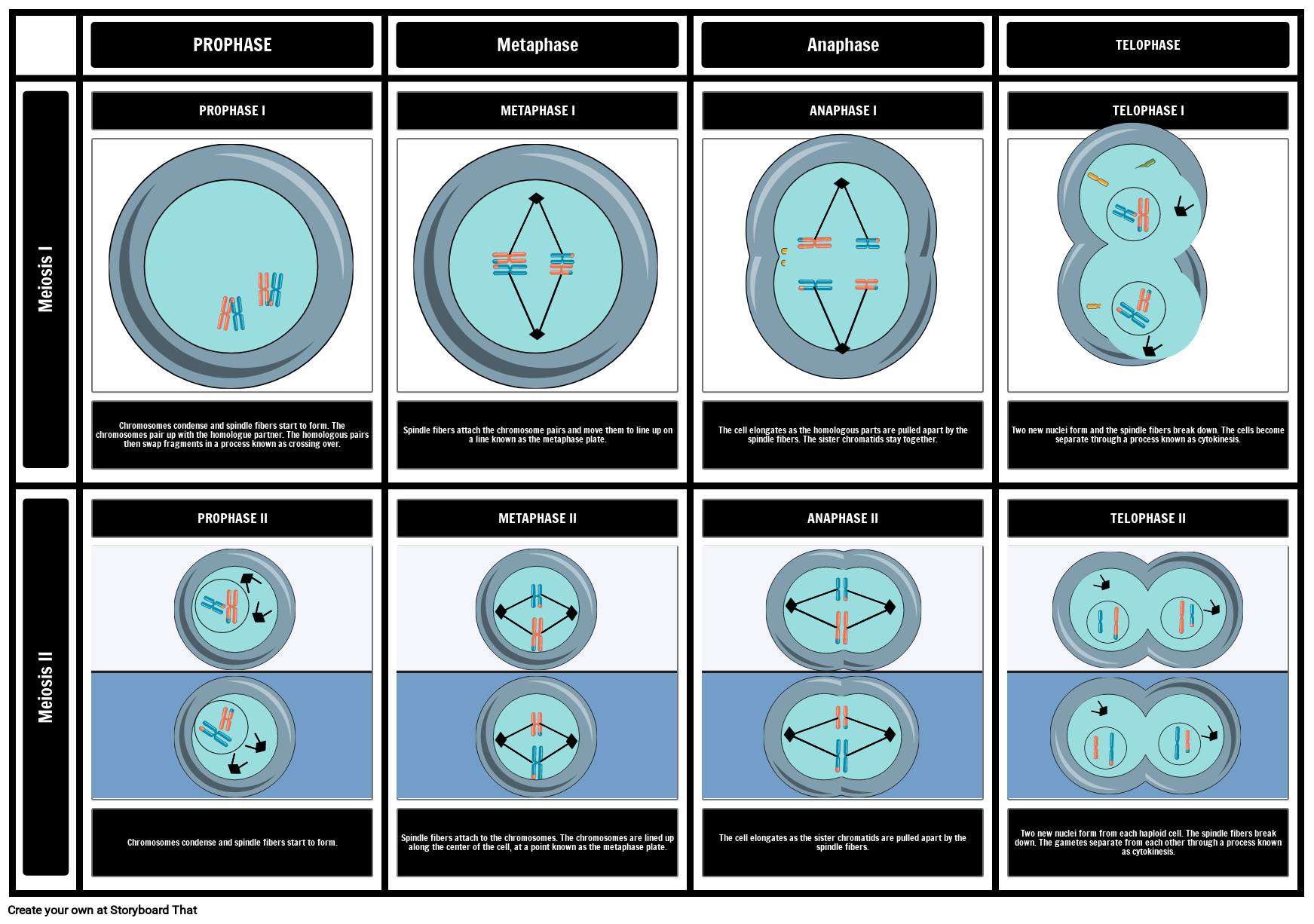
Chromosomes condense and spindle fibers start to form. The chromosomes pair up with the homologue partner. The homologous pairs then swap fragments in a process known as crossing over.
Spindle fibers attach the chromosome pairs and move them to line up on a line known as the metaphase plate.
The cell elongates as the homologous parts are pulled apart by the spindle fibers. The sister chromatids stay together.
Two new nuclei form and the spindle fibers break down. The cells become separate through a process known as cytokinesis.
Chromosomes condense and spindle fibers start to form.
Spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes. The chromosomes are lined up along the center of the cell, at a point known as the metaphase plate.
The cell elongates as the sister chromatids are pulled apart by the spindle fibers.
Two new nuclei form from each haploid cell. The spindle fibers break down. The gametes separate from each other through a process known as cytokinesis.
PROPHASE
Metaphase
Anaphase
TELOPHASE
Meiosis II
Meiosis I
PROPHASE I
METAPHASE I
ANAPHASE I
TELOPHASE I
PROPHASE II
METAPHASE II
ANAPHASE II
TELOPHASE II
Chromosomes condense and spindle fibers start to form. The chromosomes pair up with the homologue partner. The homologous pairs then swap fragments in a process known as crossing over.
Spindle fibers attach the chromosome pairs and move them to line up on a line known as the metaphase plate.
The cell elongates as the homologous parts are pulled apart by the spindle fibers. The sister chromatids stay together.
Two new nuclei form and the spindle fibers break down. The cells become separate through a process known as cytokinesis.
Chromosomes condense and spindle fibers start to form.
Spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes. The chromosomes are lined up along the center of the cell, at a point known as the metaphase plate.
The cell elongates as the sister chromatids are pulled apart by the spindle fibers.
Two new nuclei form from each haploid cell. The spindle fibers break down. The gametes separate from each other through a process known as cytokinesis.
PROPHASE
Metaphase
Anaphase
TELOPHASE
Meiosis II
Meiosis I
PROPHASE I
METAPHASE I
ANAPHASE I
TELOPHASE I
PROPHASE II
METAPHASE II
ANAPHASE II
TELOPHASE II
Chromosomes condense and spindle fibers start to form. The chromosomes pair up with the homologue partner. The homologous pairs then swap fragments in a process known as crossing over.
Spindle fibers attach the chromosome pairs and move them to line up on a line known as the metaphase plate.
The cell elongates as the homologous parts are pulled apart by the spindle fibers. The sister chromatids stay together.
Two new nuclei form and the spindle fibers break down. The cells become separate through a process known as cytokinesis.
Chromosomes condense and spindle fibers start to form.
Spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes. The chromosomes are lined up along the center of the cell, at a point known as the metaphase plate.
The cell elongates as the sister chromatids are pulled apart by the spindle fibers.
Two new nuclei form from each haploid cell. The spindle fibers break down. The gametes separate from each other through a process known as cytokinesis.
PROPHASE
Metaphase
Anaphase
TELOPHASE
Meiosis II
Meiosis I
PROPHASE I
METAPHASE I
ANAPHASE I
TELOPHASE I
PROPHASE II
METAPHASE II
ANAPHASE II
TELOPHASE II
Chromosomes condense and spindle fibers start to form. The chromosomes pair up with the homologue partner. The homologous pairs then swap fragments in a process known as crossing over.
Spindle fibers attach the chromosome pairs and move them to line up on a line known as the metaphase plate.
The cell elongates as the homologous parts are pulled apart by the spindle fibers. The sister chromatids stay together.
Two new nuclei form and the spindle fibers break down. The cells become separate through a process known as cytokinesis.
Chromosomes condense and spindle fibers start to form.
Spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes. The chromosomes are lined up along the center of the cell, at a point known as the metaphase plate.
The cell elongates as the sister chromatids are pulled apart by the spindle fibers.
Two new nuclei form from each haploid cell. The spindle fibers break down. The gametes separate from each other through a process known as cytokinesis.
PROPHASE
Metaphase
Anaphase
TELOPHASE
Meiosis II
Meiosis I
PROPHASE I
METAPHASE I
ANAPHASE I
TELOPHASE I
PROPHASE II
METAPHASE II
ANAPHASE II
TELOPHASE II
Chromosomes condense and spindle fibers start to form. The chromosomes pair up with the homologue partner. The homologous pairs then swap fragments in a process known as crossing over.
Spindle fibers attach the chromosome pairs and move them to line up on a line known as the metaphase plate.
The cell elongates as the homologous parts are pulled apart by the spindle fibers. The sister chromatids stay together.
Two new nuclei form and the spindle fibers break down. The cells become separate through a process known as cytokinesis.
Chromosomes condense and spindle fibers start to form.
Spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes. The chromosomes are lined up along the center of the cell, at a point known as the metaphase plate.
The cell elongates as the sister chromatids are pulled apart by the spindle fibers.
Two new nuclei form from each haploid cell. The spindle fibers break down. The gametes separate from each other through a process known as cytokinesis.
PROPHASE
Metaphase
Anaphase
TELOPHASE
Meiosis II
Meiosis I
PROPHASE I
METAPHASE I
ANAPHASE I
TELOPHASE I
PROPHASE II
METAPHASE II
ANAPHASE II
TELOPHASE II
Chromosomes condense and spindle fibers start to form. The chromosomes pair up with the homologue partner. The homologous pairs then swap fragments in a process known as crossing over.
Spindle fibers attach the chromosome pairs and move them to line up on a line known as the metaphase plate.
The cell elongates as the homologous parts are pulled apart by the spindle fibers. The sister chromatids stay together.
Two new nuclei form and the spindle fibers break down. The cells become separate through a process known as cytokinesis.
Chromosomes condense and spindle fibers start to form.
Spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes. The chromosomes are lined up along the center of the cell, at a point known as the metaphase plate.
The cell elongates as the sister chromatids are pulled apart by the spindle fibers.
Two new nuclei form from each haploid cell. The spindle fibers break down. The gametes separate from each other through a process known as cytokinesis.
PROPHASE
Metaphase
Anaphase
TELOPHASE
Meiosis II
Meiosis I
PROPHASE I
METAPHASE I
ANAPHASE I
TELOPHASE I
PROPHASE II
METAPHASE II
ANAPHASE II
TELOPHASE II
Chromosomes condense and spindle fibers start to form. The chromosomes pair up with the homologue partner. The homologous pairs then swap fragments in a process known as crossing over.
Spindle fibers attach the chromosome pairs and move them to line up on a line known as the metaphase plate.
The cell elongates as the homologous parts are pulled apart by the spindle fibers. The sister chromatids stay together.
Two new nuclei form and the spindle fibers break down. The cells become separate through a process known as cytokinesis.
Chromosomes condense and spindle fibers start to form.
Spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes. The chromosomes are lined up along the center of the cell, at a point known as the metaphase plate.
The cell elongates as the sister chromatids are pulled apart by the spindle fibers.
Two new nuclei form from each haploid cell. The spindle fibers break down. The gametes separate from each other through a process known as cytokinesis.
PROPHASE
Metaphase
Anaphase
TELOPHASE
Meiosis II
Meiosis I
PROPHASE I
METAPHASE I
ANAPHASE I
TELOPHASE I
PROPHASE II
METAPHASE II
ANAPHASE II
TELOPHASE II
Chromosomes condense and spindle fibers start to form. The chromosomes pair up with the homologue partner. The homologous pairs then swap fragments in a process known as crossing over.
Spindle fibers attach the chromosome pairs and move them to line up on a line known as the metaphase plate.
The cell elongates as the homologous parts are pulled apart by the spindle fibers. The sister chromatids stay together.
Two new nuclei form and the spindle fibers break down. The cells become separate through a process known as cytokinesis.
Chromosomes condense and spindle fibers start to form.
Spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes. The chromosomes are lined up along the center of the cell, at a point known as the metaphase plate.
The cell elongates as the sister chromatids are pulled apart by the spindle fibers.
Two new nuclei form from each haploid cell. The spindle fibers break down. The gametes separate from each other through a process known as cytokinesis.
PROPHASE
Metaphase
Anaphase
TELOPHASE
Meiosis II
Meiosis I
PROPHASE I
METAPHASE I
ANAPHASE I
TELOPHASE I
PROPHASE II
METAPHASE II
ANAPHASE II
TELOPHASE II
Chromosomes condense and spindle fibers start to form. The chromosomes pair up with the homologue partner. The homologous pairs then swap fragments in a process known as crossing over.
Spindle fibers attach the chromosome pairs and move them to line up on a line known as the metaphase plate.
The cell elongates as the homologous parts are pulled apart by the spindle fibers. The sister chromatids stay together.
Two new nuclei form and the spindle fibers break down. The cells become separate through a process known as cytokinesis.
Chromosomes condense and spindle fibers start to form.
Spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes. The chromosomes are lined up along the center of the cell, at a point known as the metaphase plate.
The cell elongates as the sister chromatids are pulled apart by the spindle fibers.
Two new nuclei form from each haploid cell. The spindle fibers break down. The gametes separate from each other through a process known as cytokinesis.
PROPHASE
Metaphase
Anaphase
TELOPHASE
Meiosis II
Meiosis I
Storyboard Text
- Meiosis I
- PROPHASE I
- PROPHASE
- METAPHASE I
- Metaphase
- ANAPHASE I
- Anaphase
- TELOPHASE I
- TELOPHASE
- Chromosomes condense and spindle fibers start to form. The chromosomes pair up with the homologue partner. The homologous pairs then swap fragments in a process known as crossing over.
- PROPHASE II
- Spindle fibers attach the chromosome pairs and move them to line up on a line known as the metaphase plate.
- METAPHASE II
- The cell elongates as the homologous parts are pulled apart by the spindle fibers. The sister chromatids stay together.
- ANAPHASE II
- Two new nuclei form and the spindle fibers break down. The cells become separate through a process known as cytokinesis.
- TELOPHASE II
- Meiosis II
- Chromosomes condense and spindle fibers start to form.
- Spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes. The chromosomes are lined up along the center of the cell, at a point known as the metaphase plate.
- The cell elongates as the sister chromatids are pulled apart by the spindle fibers.
- Two new nuclei form from each haploid cell. The spindle fibers break down. The gametes separate from each other through a process known as cytokinesis.



