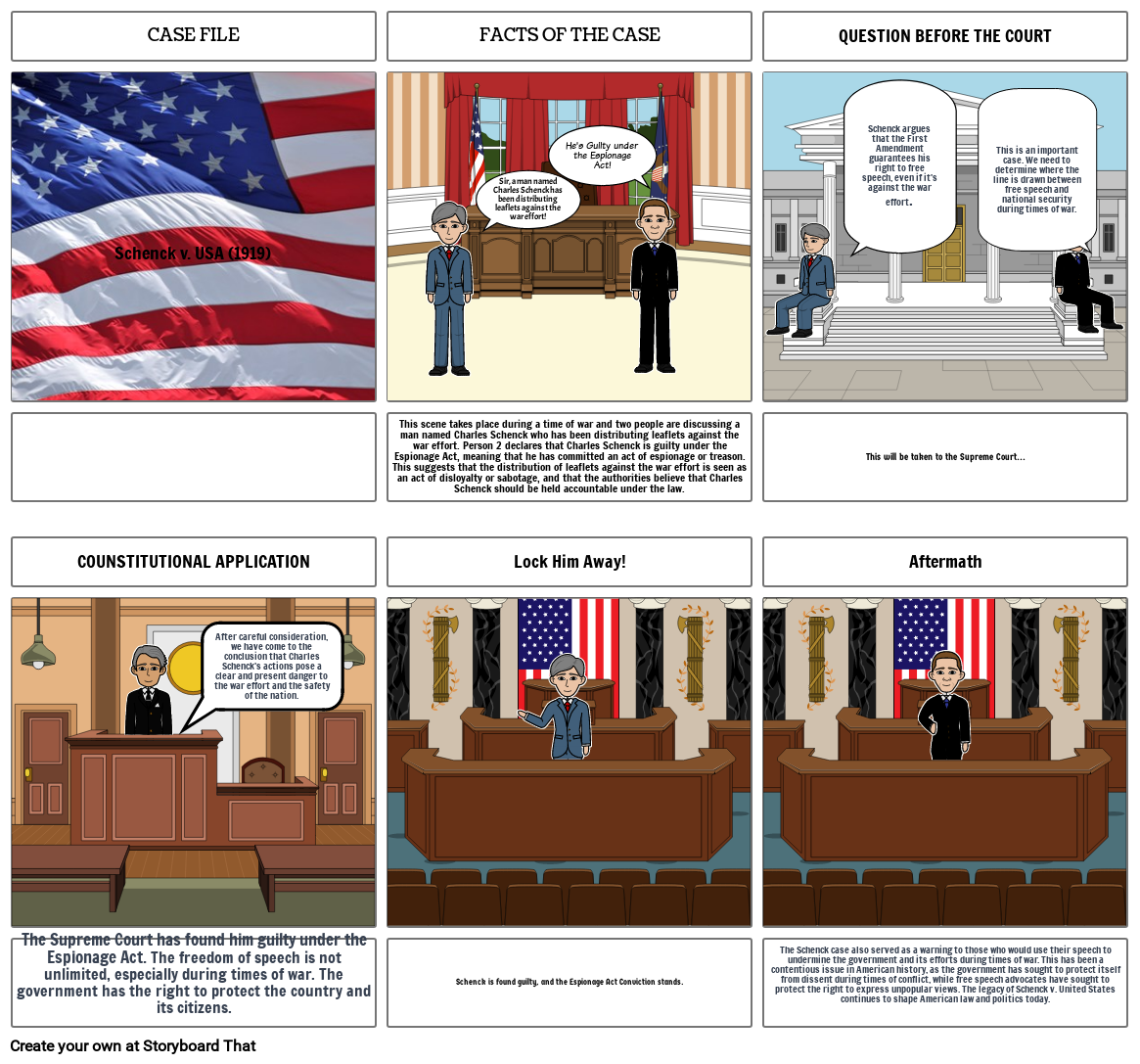
Schenck vs. USA
CASE FILE
FACTS OF THE CASE
QUESTION BEFORE THE COURT
COUNSTITUTIONAL APPLICATION
Lock Him Away!
Aftermath
This scene takes place during a time of war and two people are discussing a man named Charles Schenck who has been distributing leaflets against the war effort. Person 2 declares that Charles Schenck is guilty under the Espionage Act, meaning that he has committed an act of espionage or treason. This suggests that the distribution of leaflets against the war effort is seen as an act of disloyalty or sabotage, and that the authorities believe that Charles Schenck should be held accountable under the law.
This will be taken to the Supreme Court...
The Supreme Court has found him guilty under the Espionage Act. The freedom of speech is not unlimited, especially during times of war. The government has the right to protect the country and its citizens.
Schenck is found guilty, and the Espionage Act Conviction stands.
The Schenck case also served as a warning to those who would use their speech to undermine the government and its efforts during times of war. This has been a contentious issue in American history, as the government has sought to protect itself from dissent during times of conflict, while free speech advocates have sought to protect the right to express unpopular views. The legacy of Schenck v. United States continues to shape American law and politics today.
Schenck v. USA (1919)
After careful consideration, we have come to the conclusion that Charles Schenck's actions pose a clear and present danger to the war effort and the safety of the nation.
Sir, a man named Charles Schenck has been distributing leaflets against the war effort!
He's Guilty under the Espionage Act!
This is an important case. We need to determine where the line is drawn between free speech and national security during times of war.
Schenck argues that the First Amendment guarantees his right to free speech, even if it's against the war effort.
CASE FILE
FACTS OF THE CASE
QUESTION BEFORE THE COURT
COUNSTITUTIONAL APPLICATION
Lock Him Away!
Aftermath
This scene takes place during a time of war and two people are discussing a man named Charles Schenck who has been distributing leaflets against the war effort. Person 2 declares that Charles Schenck is guilty under the Espionage Act, meaning that he has committed an act of espionage or treason. This suggests that the distribution of leaflets against the war effort is seen as an act of disloyalty or sabotage, and that the authorities believe that Charles Schenck should be held accountable under the law.
This will be taken to the Supreme Court...
The Supreme Court has found him guilty under the Espionage Act. The freedom of speech is not unlimited, especially during times of war. The government has the right to protect the country and its citizens.
Schenck is found guilty, and the Espionage Act Conviction stands.
The Schenck case also served as a warning to those who would use their speech to undermine the government and its efforts during times of war. This has been a contentious issue in American history, as the government has sought to protect itself from dissent during times of conflict, while free speech advocates have sought to protect the right to express unpopular views. The legacy of Schenck v. United States continues to shape American law and politics today.
Schenck v. USA (1919)
After careful consideration, we have come to the conclusion that Charles Schenck's actions pose a clear and present danger to the war effort and the safety of the nation.
Sir, a man named Charles Schenck has been distributing leaflets against the war effort!
He's Guilty under the Espionage Act!
This is an important case. We need to determine where the line is drawn between free speech and national security during times of war.
Schenck argues that the First Amendment guarantees his right to free speech, even if it's against the war effort.
CASE FILE
FACTS OF THE CASE
QUESTION BEFORE THE COURT
COUNSTITUTIONAL APPLICATION
Lock Him Away!
Aftermath
This scene takes place during a time of war and two people are discussing a man named Charles Schenck who has been distributing leaflets against the war effort. Person 2 declares that Charles Schenck is guilty under the Espionage Act, meaning that he has committed an act of espionage or treason. This suggests that the distribution of leaflets against the war effort is seen as an act of disloyalty or sabotage, and that the authorities believe that Charles Schenck should be held accountable under the law.
This will be taken to the Supreme Court...
The Supreme Court has found him guilty under the Espionage Act. The freedom of speech is not unlimited, especially during times of war. The government has the right to protect the country and its citizens.
Schenck is found guilty, and the Espionage Act Conviction stands.
The Schenck case also served as a warning to those who would use their speech to undermine the government and its efforts during times of war. This has been a contentious issue in American history, as the government has sought to protect itself from dissent during times of conflict, while free speech advocates have sought to protect the right to express unpopular views. The legacy of Schenck v. United States continues to shape American law and politics today.
Schenck v. USA (1919)
After careful consideration, we have come to the conclusion that Charles Schenck's actions pose a clear and present danger to the war effort and the safety of the nation.
Sir, a man named Charles Schenck has been distributing leaflets against the war effort!
He's Guilty under the Espionage Act!
This is an important case. We need to determine where the line is drawn between free speech and national security during times of war.
Schenck argues that the First Amendment guarantees his right to free speech, even if it's against the war effort.
CASE FILE
FACTS OF THE CASE
QUESTION BEFORE THE COURT
COUNSTITUTIONAL APPLICATION
Lock Him Away!
Aftermath
This scene takes place during a time of war and two people are discussing a man named Charles Schenck who has been distributing leaflets against the war effort. Person 2 declares that Charles Schenck is guilty under the Espionage Act, meaning that he has committed an act of espionage or treason. This suggests that the distribution of leaflets against the war effort is seen as an act of disloyalty or sabotage, and that the authorities believe that Charles Schenck should be held accountable under the law.
This will be taken to the Supreme Court...
The Supreme Court has found him guilty under the Espionage Act. The freedom of speech is not unlimited, especially during times of war. The government has the right to protect the country and its citizens.
Schenck is found guilty, and the Espionage Act Conviction stands.
The Schenck case also served as a warning to those who would use their speech to undermine the government and its efforts during times of war. This has been a contentious issue in American history, as the government has sought to protect itself from dissent during times of conflict, while free speech advocates have sought to protect the right to express unpopular views. The legacy of Schenck v. United States continues to shape American law and politics today.
Schenck v. USA (1919)
After careful consideration, we have come to the conclusion that Charles Schenck's actions pose a clear and present danger to the war effort and the safety of the nation.
Sir, a man named Charles Schenck has been distributing leaflets against the war effort!
He's Guilty under the Espionage Act!
This is an important case. We need to determine where the line is drawn between free speech and national security during times of war.
Schenck argues that the First Amendment guarantees his right to free speech, even if it's against the war effort.
CASE FILE
FACTS OF THE CASE
QUESTION BEFORE THE COURT
COUNSTITUTIONAL APPLICATION
Lock Him Away!
Aftermath
This scene takes place during a time of war and two people are discussing a man named Charles Schenck who has been distributing leaflets against the war effort. Person 2 declares that Charles Schenck is guilty under the Espionage Act, meaning that he has committed an act of espionage or treason. This suggests that the distribution of leaflets against the war effort is seen as an act of disloyalty or sabotage, and that the authorities believe that Charles Schenck should be held accountable under the law.
This will be taken to the Supreme Court...
The Supreme Court has found him guilty under the Espionage Act. The freedom of speech is not unlimited, especially during times of war. The government has the right to protect the country and its citizens.
Schenck is found guilty, and the Espionage Act Conviction stands.
The Schenck case also served as a warning to those who would use their speech to undermine the government and its efforts during times of war. This has been a contentious issue in American history, as the government has sought to protect itself from dissent during times of conflict, while free speech advocates have sought to protect the right to express unpopular views. The legacy of Schenck v. United States continues to shape American law and politics today.
Schenck v. USA (1919)
After careful consideration, we have come to the conclusion that Charles Schenck's actions pose a clear and present danger to the war effort and the safety of the nation.
Sir, a man named Charles Schenck has been distributing leaflets against the war effort!
He's Guilty under the Espionage Act!
This is an important case. We need to determine where the line is drawn between free speech and national security during times of war.
Schenck argues that the First Amendment guarantees his right to free speech, even if it's against the war effort.
CASE FILE
FACTS OF THE CASE
QUESTION BEFORE THE COURT
COUNSTITUTIONAL APPLICATION
Lock Him Away!
Aftermath
This scene takes place during a time of war and two people are discussing a man named Charles Schenck who has been distributing leaflets against the war effort. Person 2 declares that Charles Schenck is guilty under the Espionage Act, meaning that he has committed an act of espionage or treason. This suggests that the distribution of leaflets against the war effort is seen as an act of disloyalty or sabotage, and that the authorities believe that Charles Schenck should be held accountable under the law.
This will be taken to the Supreme Court...
The Supreme Court has found him guilty under the Espionage Act. The freedom of speech is not unlimited, especially during times of war. The government has the right to protect the country and its citizens.
Schenck is found guilty, and the Espionage Act Conviction stands.
The Schenck case also served as a warning to those who would use their speech to undermine the government and its efforts during times of war. This has been a contentious issue in American history, as the government has sought to protect itself from dissent during times of conflict, while free speech advocates have sought to protect the right to express unpopular views. The legacy of Schenck v. United States continues to shape American law and politics today.
Schenck v. USA (1919)
After careful consideration, we have come to the conclusion that Charles Schenck's actions pose a clear and present danger to the war effort and the safety of the nation.
Sir, a man named Charles Schenck has been distributing leaflets against the war effort!
He's Guilty under the Espionage Act!
This is an important case. We need to determine where the line is drawn between free speech and national security during times of war.
Schenck argues that the First Amendment guarantees his right to free speech, even if it's against the war effort.
CASE FILE
FACTS OF THE CASE
QUESTION BEFORE THE COURT
COUNSTITUTIONAL APPLICATION
Lock Him Away!
Aftermath
This scene takes place during a time of war and two people are discussing a man named Charles Schenck who has been distributing leaflets against the war effort. Person 2 declares that Charles Schenck is guilty under the Espionage Act, meaning that he has committed an act of espionage or treason. This suggests that the distribution of leaflets against the war effort is seen as an act of disloyalty or sabotage, and that the authorities believe that Charles Schenck should be held accountable under the law.
This will be taken to the Supreme Court...
The Supreme Court has found him guilty under the Espionage Act. The freedom of speech is not unlimited, especially during times of war. The government has the right to protect the country and its citizens.
Schenck is found guilty, and the Espionage Act Conviction stands.
The Schenck case also served as a warning to those who would use their speech to undermine the government and its efforts during times of war. This has been a contentious issue in American history, as the government has sought to protect itself from dissent during times of conflict, while free speech advocates have sought to protect the right to express unpopular views. The legacy of Schenck v. United States continues to shape American law and politics today.
Schenck v. USA (1919)
After careful consideration, we have come to the conclusion that Charles Schenck's actions pose a clear and present danger to the war effort and the safety of the nation.
Sir, a man named Charles Schenck has been distributing leaflets against the war effort!
He's Guilty under the Espionage Act!
This is an important case. We need to determine where the line is drawn between free speech and national security during times of war.
Schenck argues that the First Amendment guarantees his right to free speech, even if it's against the war effort.
Storyboard Text
- CASE FILE
- Schenck v. USA (1919)
- FACTS OF THE CASE
- Sir, a man named Charles Schenck has been distributing leaflets against the war effort!
- He's Guilty under the Espionage Act!
- QUESTION BEFORE THE COURT
- Schenck argues that the First Amendment guarantees his right to free speech, even if it's against the war effort.
- This is an important case. We need to determine where the line is drawn between free speech and national security during times of war.
-
- COUNSTITUTIONAL APPLICATION
- After careful consideration, we have come to the conclusion that Charles Schenck's actions pose a clear and present danger to the war effort and the safety of the nation.
- This scene takes place during a time of war and two people are discussing a man named Charles Schenck who has been distributing leaflets against the war effort. Person 2 declares that Charles Schenck is guilty under the Espionage Act, meaning that he has committed an act of espionage or treason. This suggests that the distribution of leaflets against the war effort is seen as an act of disloyalty or sabotage, and that the authorities believe that Charles Schenck should be held accountable under the law.
- Lock Him Away!
- This will be taken to the Supreme Court...
- Aftermath
- The Supreme Court has found him guilty under the Espionage Act. The freedom of speech is not unlimited, especially during times of war. The government has the right to protect the country and its citizens.
- Schenck is found guilty, and the Espionage Act Conviction stands.
- The Schenck case also served as a warning to those who would use their speech to undermine the government and its efforts during times of war. This has been a contentious issue in American history, as the government has sought to protect itself from dissent during times of conflict, while free speech advocates have sought to protect the right to express unpopular views. The legacy of Schenck v. United States continues to shape American law and politics today.



