The Life Cycle of a Star
Storyboard Text
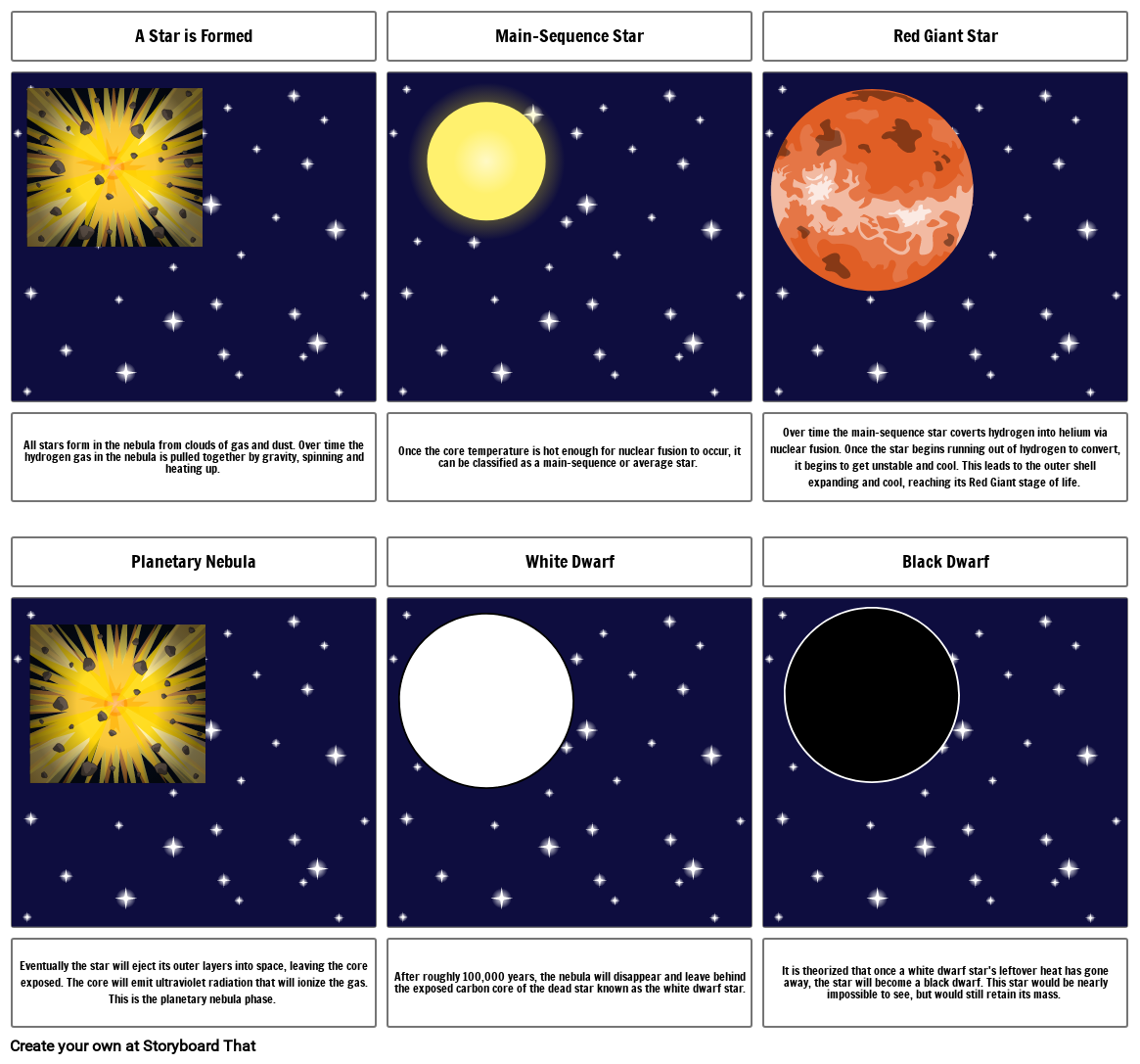
- A Star is Formed
- Main-Sequence Star
- Red Giant Star
- All stars form in the nebula from clouds of gas and dust. Over time the hydrogen gas in the nebula is pulled together by gravity, spinning and heating up. 
- Planetary Nebula
- Once the core temperature is hot enough for nuclear fusion to occur, it can be classified as a main-sequence or average star. 
- White Dwarf
- Over time the main-sequence star coverts hydrogen into helium via nuclear fusion. Once the star begins running out of hydrogen to convert, it begins to get unstable and cool. This leads to the outer shell expanding and cool, reaching its Red Giant stage of life. 
- Black Dwarf
- Eventually the star will eject its outer layers into space, leaving the core exposed. The core will emit ultraviolet radiation that will ionize the gas. This is the planetary nebula phase. 
- After roughly 100,000 years, the nebula will disappear and leave behind the exposed carbon core of the dead star known as the white dwarf star.
- It is theorized that once a white dwarf star's leftover heat has gone away, the star will become a black dwarf. This star would be nearly impossible to see, but would still retain its mass. 
Over 30 Million Storyboards Created

