Constitutional Convention Compromise
Storyboard Text
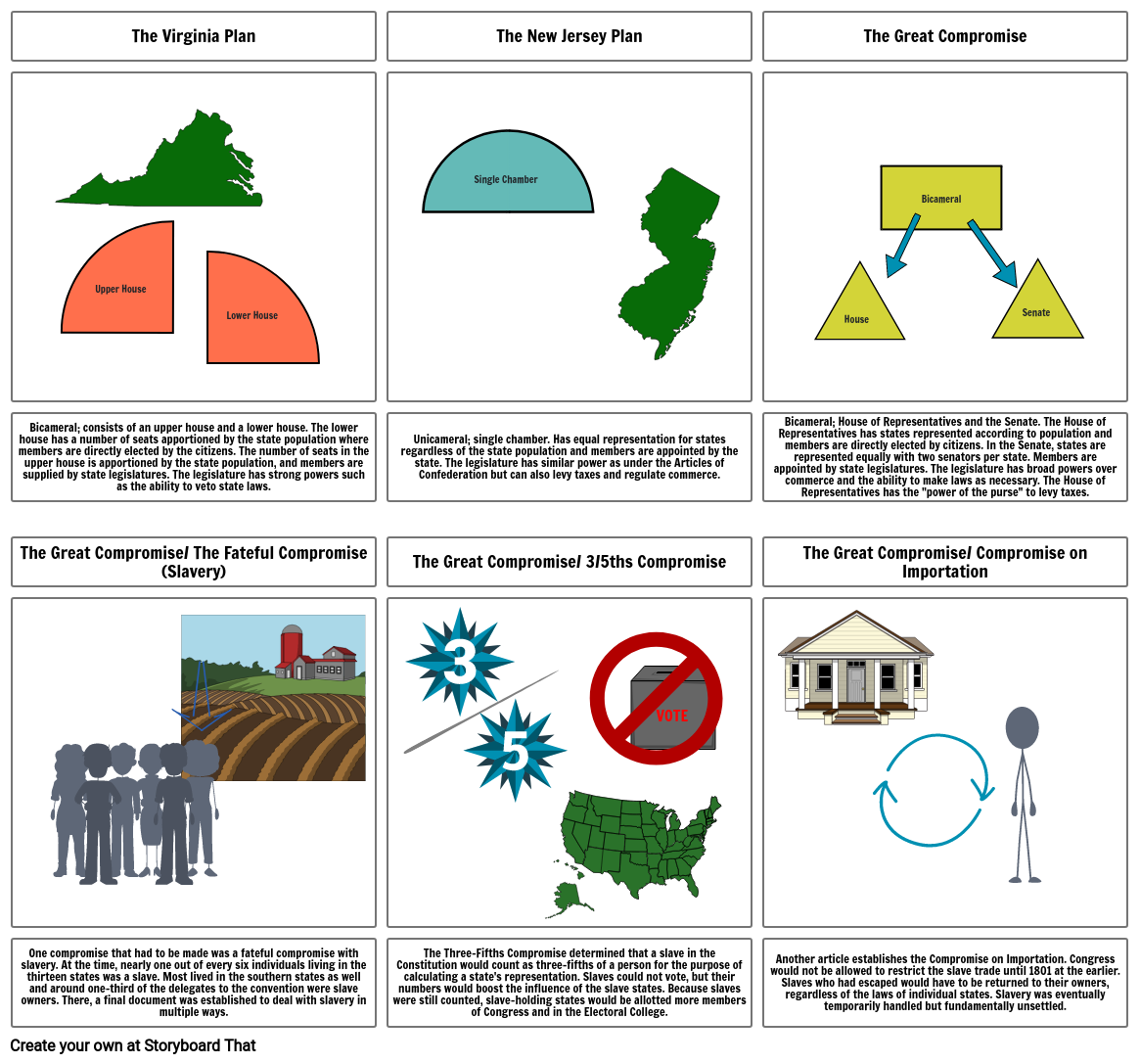
- The Virginia Plan
- Upper House
- Lower House
- The New Jersey Plan
- Single Chamber
- The Great Compromise
- House
- Bicameral
- Senate
- Bicameral; consists of an upper house and a lower house. The lower house has a number of seats apportioned by the state population where members are directly elected by the citizens. The number of seats in the upper house is apportioned by the state population, and members are supplied by state legislatures. The legislature has strong powers such as the ability to veto state laws.
- The Great Compromise/ The Fateful Compromise (Slavery)
- Unicameral; single chamber. Has equal representation for states regardless of the state population and members are appointed by the state. The legislature has similar power as under the Articles of Confederation but can also levy taxes and regulate commerce.
- The Great Compromise/ 3/5ths Compromise
- VOTE
- Bicameral; House of Representatives and the Senate. The House of Representatives has states represented according to population and members are directly elected by citizens. In the Senate, states are represented equally with two senators per state. Members are appointed by state legislatures. The legislature has broad powers over commerce and the ability to make laws as necessary. The House of Representatives has the "power of the purse" to levy taxes.
- The Great Compromise/ Compromise on Importation
- One compromise that had to be made was a fateful compromise with slavery. At the time, nearly one out of every six individuals living in the thirteen states was a slave. Most lived in the southern states as well and around one-third of the delegates to the convention were slave owners. There, a final document was established to deal with slavery in multiple ways.
- The Three-Fifths Compromise determined that a slave in the Constitution would count as three-fifths of a person for the purpose of calculating a state's representation. Slaves could not vote, but their numbers would boost the influence of the slave states. Because slaves were still counted, slave-holding states would be allotted more members of Congress and in the Electoral College.
- Another article establishes the Compromise on Importation. Congress would not be allowed to restrict the slave trade until 1801 at the earlier. Slaves who had escaped would have to be returned to their owners, regardless of the laws of individual states. Slavery was eventually temporarily handled but fundamentally unsettled.
Over 30 Million Storyboards Created

