Nerve impulse
Storyboard Text
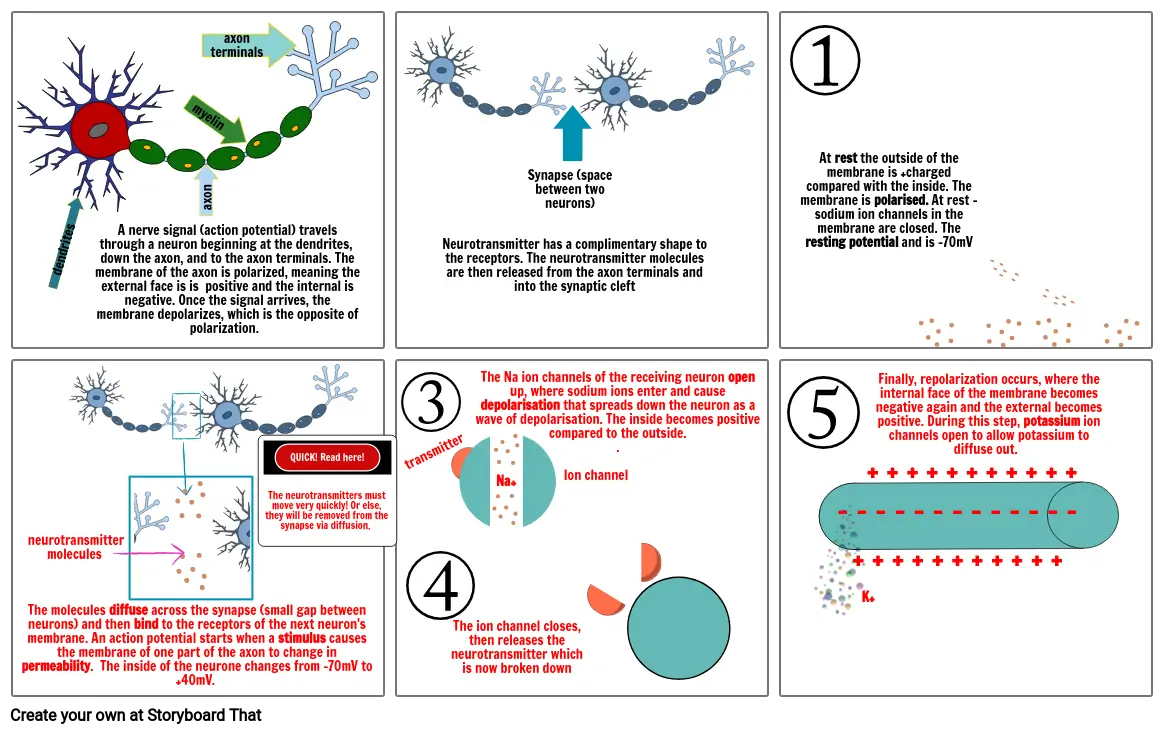
- dendrites
- A nerve signal (action potential) travels through a neuron beginning at the dendrites, down the axon, and to the axon terminals. The membrane of the axon is polarized, meaning the external face is is positive and the internal is negative. Once the signal arrives, the membrane depolarizes, which is the opposite of polarization.
- axon
- myelin
- axon terminals
- Neurotransmitter has a complimentary shape to the receptors. The neurotransmitter molecules are then released from the axon terminals and into the synaptic cleft
- Synapse (space between two neurons)
-
- At rest the outside of the membrane is +charged compared with the inside. The membrane is polarised. At rest – sodium ion channels in the membrane are closed. The resting potential and is -70mV
- neurotransmitter molecules
- The molecules diffuse across the synapse (small gap between neurons) and then bind to the receptors of the next neuron's membrane. An action potential starts when a stimulus causes the membrane of one part of the axon to change in permeability. The inside of the neurone changes from -70mV to +40mV.
- QUICK! Read here! The neurotransmitters must move very quickly! Or else, they will be removed from the synapse via diffusion.
- transmitter
- The ion channel closes, then releases the neurotransmitter which is now broken down
-
- Na+
- The Na ion channels of the receiving neuron open up, where sodium ions enter and cause depolarisation that spreads down the neuron as a wave of depolarisation. The inside becomes positive compared to the outside..
- Ion channel
- - - - - - - - - - - - - -
- K+
- + + + + + + + + + + +
- + + + + + + + + + + +
- Finally, repolarization occurs, where the internal face of the membrane becomes negative again and the external becomes positive. During this step, potassium ion channels open to allow potassium to diffuse out.
Over 30 Million Storyboards Created
No Downloads, No Credit Card, and No Login Needed to Try!
