Evolution of Philippine Constitution
Storyboard Text
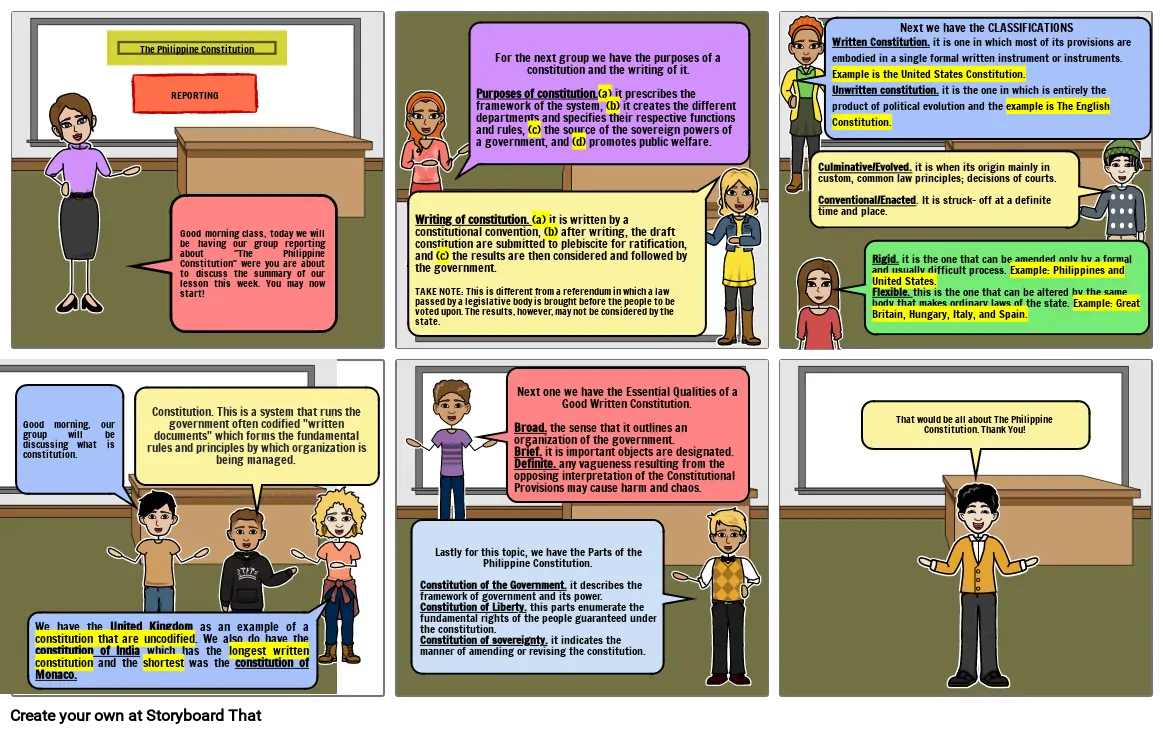
- The Philippine Constitution
- Good morning class, today we will be having our group reporting about "The Philippine Constitution" were you are about to discuss the summary of our lesson this week. You may now start!
- REPORTING
- Writing of constitution. (a) it is written by a constitutional convention, (b) after writing, the draft constitution are submitted to plebiscite for ratification, and (c) the results are then considered and followed by the government.TAKE NOTE: This is different from a referendum in which a law passed by a legislative body is brought before the people to be voted upon. The results, however, may not be considered by the state.
- For the next group we have the purposes of a constitution and the writing of it.Purposes of constitution.(a) it prescribes the framework of the system, (b) it creates the different departments and specifies their respective functions and rules, (c) the source of the sovereign powers of a government, and (d) promotes public welfare.
- The Philippine Constitution
- GROUP 2
- Next we have the CLASSIFICATIONSWritten Constitution. it is one in which most of its provisions are embodied in a single formal written instrument or instruments. Example is the United States Constitution.Unwritten constitution. it is the one in which is entirely the product of political evolution and the example is The English Constitution.
- Rigid. it is the one that can be amended only by a formal and usually difficult process. Example: Philippines and United States.Flexible. this is the one that can be altered by the same body that makes ordinary laws of the state. Example: Great Britain, Hungary, Italy, and Spain.
- Culminative/Evolved. it is when its origin mainly in custom, common law principles; decisions of courts.Conventional/Enacted. It is struck- off at a definite time and place.
- Good morning, our group will be discussing what is constitution.
- We have the United Kingdom as an example of a constitution that are uncodified. We also do have the constitution of India which has the longest written constitution and the shortest was the constitution of Monaco.
- Constitution. This is a system that runs the government often codified "written documents" which forms the fundamental rules and principles by which organization is being managed.
- Next one we have the Essential Qualities of a Good Written Constitution.Broad. the sense that it outlines an organization of the government.Brief. it is important objects are designated.Definite. any vagueness resulting from the opposing interpretation of the Constitutional Provisions may cause harm and chaos.
- Lastly for this topic, we have the Parts of the Philippine Constitution. Constitution of the Government. it describes the framework of government and its power.Constitution of Liberty. this parts enumerate the fundamental rights of the people guaranteed under the constitution.Constitution of sovereignty. it indicates the manner of amending or revising the constitution.
- That would be all about The Philippine Constitution. Thank You!
Over 30 Million Storyboards Created
No Downloads, No Credit Card, and No Login Needed to Try!
