Digestive process
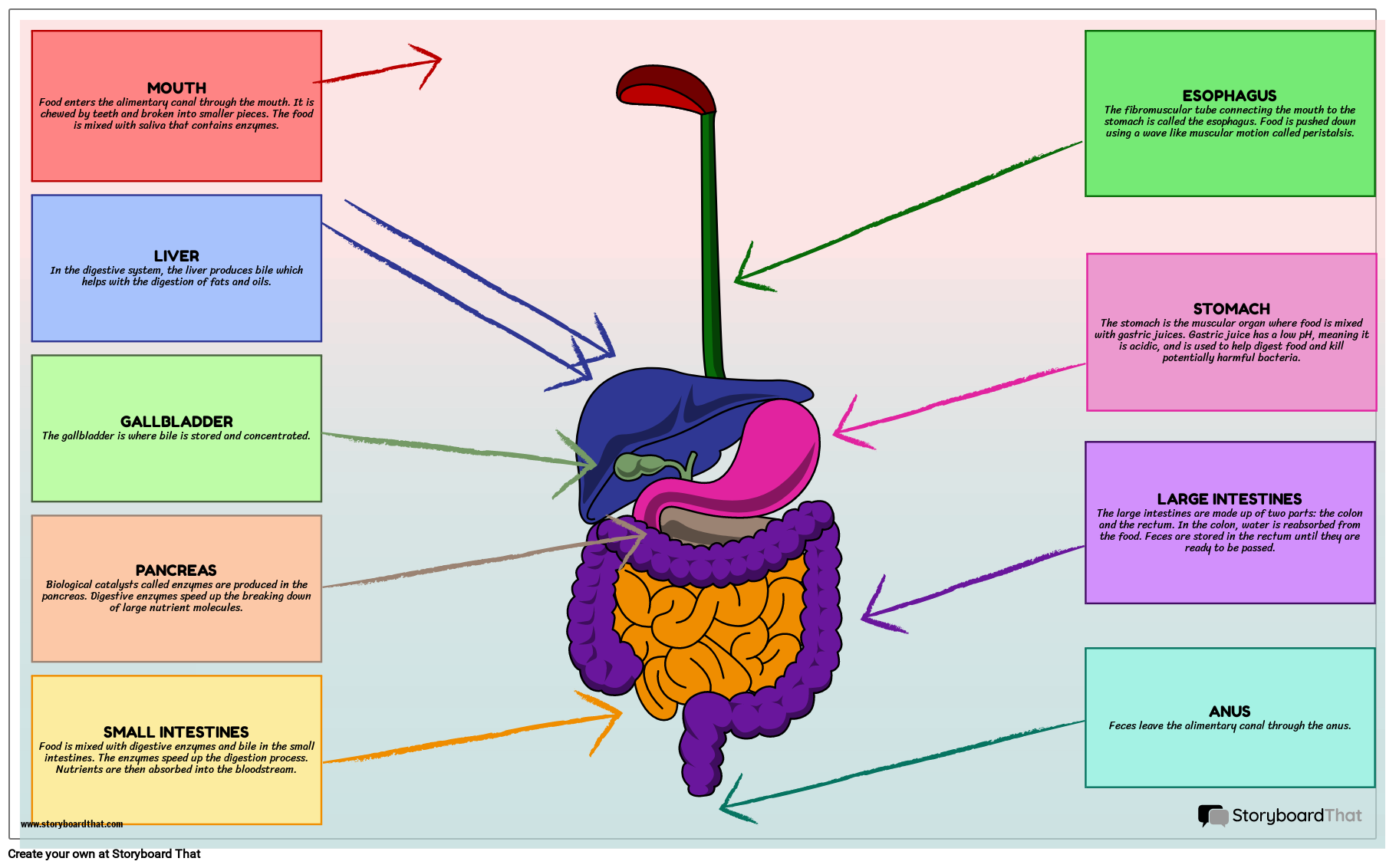
MOUTH
Food enters the alimentary canal through the mouth. It is chewed by teeth and broken into smaller pieces. The food is mixed with saliva that contains enzymes.
ESOPHAGUS
The fibromuscular tube connecting the mouth to the stomach is called the esophagus. Food is pushed down using a wave like muscular motion called peristalsis.
STOMACH
The stomach is the muscular organ where food is mixed with gastric juices. Gastric juice has a low pH, meaning it is acidic, and is used to help digest food and kill potentially harmful bacteria.
SMALL INTESTINES
Food is mixed with digestive enzymes and bile in the small intestines. The enzymes speed up the digestion process. Nutrients are then absorbed into the bloodstream.
LARGE INTESTINES
The large intestines are made up of two parts: the colon and the rectum. In the colon, water is reabsorbed from the food. Feces are stored in the rectum until they are ready to be passed.
ANUS
Feces leave the alimentary canal through the anus.
LIVER
In the digestive system, the liver produces bile which helps with the digestion of fats and oils.
GALLBLADDER
The gallbladder is where bile is stored and concentrated.
PANCREAS
Biological catalysts called enzymes are produced in the pancreas. Digestive enzymes speed up the breaking down of large nutrient molecules.
Snemalna Knjiga Besedilo
- MOUTHFood enters the alimentary canal through the mouth. It is chewed by teeth and broken into smaller pieces. The food is mixed with saliva that contains enzymes.
- LIVERIn the digestive system, the liver produces bile which helps with the digestion of fats and oils.
- GALLBLADDERThe gallbladder is where bile is stored and concentrated.
- PANCREASBiological catalysts called enzymes are produced in the pancreas. Digestive enzymes speed up the breaking down of large nutrient molecules.
- SMALL INTESTINESFood is mixed with digestive enzymes and bile in the small intestines. The enzymes speed up the digestion process. Nutrients are then absorbed into the bloodstream.
- ESOPHAGUSThe fibromuscular tube connecting the mouth to the stomach is called the esophagus. Food is pushed down using a wave like muscular motion called peristalsis.
- LARGE INTESTINESThe large intestines are made up of two parts: the colon and the rectum. In the colon, water is reabsorbed from the food. Feces are stored in the rectum until they are ready to be passed.
- ANUSFeces leave the alimentary canal through the anus.
- STOMACHThe stomach is the muscular organ where food is mixed with gastric juices. Gastric juice has a low pH, meaning it is acidic, and is used to help digest food and kill potentially harmful bacteria.


