Biology Vocab Chapter 13
Snemalna Knjiga Besedilo
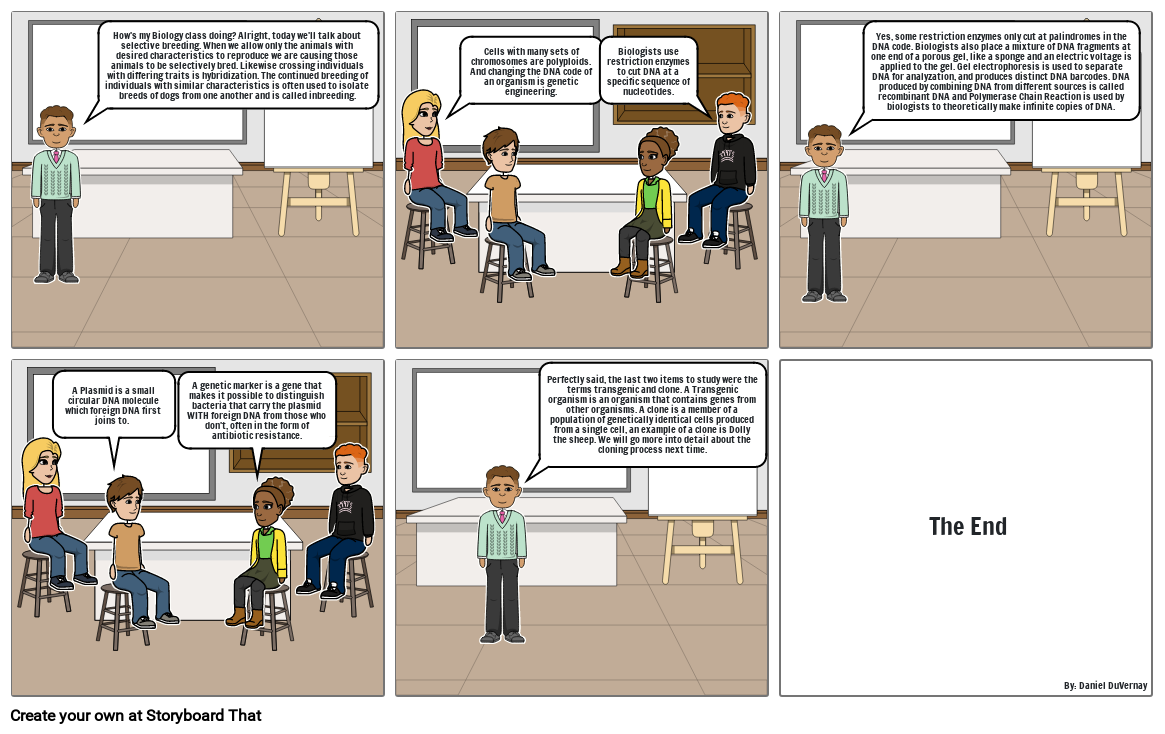
- How's my Biology class doing? Alright, today we'll talk about selective breeding. When we allow only the animals with desired characteristics to reproduce we are causing those animals to be selectively bred. Likewise crossing individuals with differing traits is hybridization. The continued breeding of individuals with similar characteristics is often used to isolate breeds of dogs from one another and is called inbreeding.
- Cells with many sets of chromosomes are polyploids. And changing the DNA code of an organism is genetic engineering.
- Biologists use restriction enzymes to cut DNA at a specific sequence of nucleotides.
- Yes, some restriction enzymes only cut at palindromes in the DNA code. Biologists also place a mixture of DNA fragments at one end of a porous gel, like a sponge and an electric voltage is applied to the gel. Gel electrophoresis is used to separate DNA for analyzation, and produces distinct DNA barcodes. DNA produced by combining DNA from different sources is called recombinant DNA and Polymerase Chain Reaction is used by biologists to theoretically make infinite copies of DNA.
- A Plasmid is a small circular DNA molecule which foreign DNA first joins to. 
- A genetic marker is a gene that makes it possible to distinguish bacteria that carry the plasmid WITH foreign DNA from those who don't, often in the form of antibiotic resistance.
- Perfectly said, the last two items to study were the terms transgenic and clone. A Transgenic organism is an organism that contains genes from other organisms. A clone is a member of a population of genetically identical cells produced from a single cell, an example of a clone is Dolly the sheep. We will go more into detail about the cloning process next time.
- The End
- By: Daniel DuVernay
Ustvarjenih več kot 30 milijonov snemalnih knjig

