Science Atomic Comic Strip
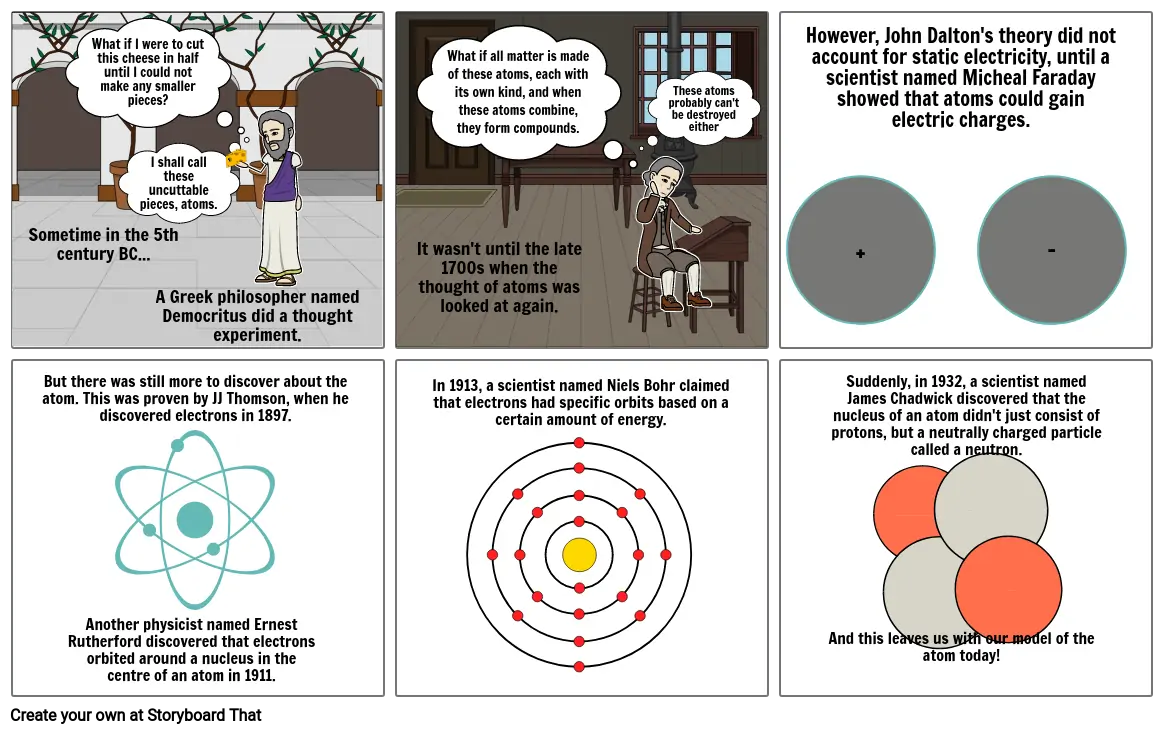
What if I were to cut this cheese in half until I could not make any smaller pieces?
I shall call these uncuttable pieces, atoms.
Sometime in the 5th century BC...
A Greek philosopher named Democritus did a thought experiment.
These atoms probably can't be destroyed either
It wasn't until the late 1700s when the thought of atoms was looked at again.
However, John Dalton's theory did not account for static electricity, until a scientist named Micheal Faraday showed that atoms could gain electric charges.
+
-
But there was still more to discover about the atom. This was proven by JJ Thomson, when he discovered electrons in 1897.
Another physicist named Ernest Rutherford discovered that electrons orbited around a nucleus in the centre of an atom in 1911.
In 1913, a scientist named Niels Bohr claimed that electrons had specific orbits based on a certain amount of energy.
Suddenly, in 1932, a scientist named James Chadwick discovered that the nucleus of an atom didn't just consist of protons, but a neutrally charged particle called a neutron.
And this leaves us with our model of the atom today!
What if I were to cut this cheese in half until I could not make any smaller pieces?
I shall call these uncuttable pieces, atoms.
Sometime in the 5th century BC...
A Greek philosopher named Democritus did a thought experiment.
These atoms probably can't be destroyed either
It wasn't until the late 1700s when the thought of atoms was looked at again.
However, John Dalton's theory did not account for static electricity, until a scientist named Micheal Faraday showed that atoms could gain electric charges.
+
-
But there was still more to discover about the atom. This was proven by JJ Thomson, when he discovered electrons in 1897.
Another physicist named Ernest Rutherford discovered that electrons orbited around a nucleus in the centre of an atom in 1911.
In 1913, a scientist named Niels Bohr claimed that electrons had specific orbits based on a certain amount of energy.
Suddenly, in 1932, a scientist named James Chadwick discovered that the nucleus of an atom didn't just consist of protons, but a neutrally charged particle called a neutron.
And this leaves us with our model of the atom today!
What if I were to cut this cheese in half until I could not make any smaller pieces?
I shall call these uncuttable pieces, atoms.
Sometime in the 5th century BC...
A Greek philosopher named Democritus did a thought experiment.
These atoms probably can't be destroyed either
It wasn't until the late 1700s when the thought of atoms was looked at again.
However, John Dalton's theory did not account for static electricity, until a scientist named Micheal Faraday showed that atoms could gain electric charges.
+
-
But there was still more to discover about the atom. This was proven by JJ Thomson, when he discovered electrons in 1897.
Another physicist named Ernest Rutherford discovered that electrons orbited around a nucleus in the centre of an atom in 1911.
In 1913, a scientist named Niels Bohr claimed that electrons had specific orbits based on a certain amount of energy.
Suddenly, in 1932, a scientist named James Chadwick discovered that the nucleus of an atom didn't just consist of protons, but a neutrally charged particle called a neutron.
And this leaves us with our model of the atom today!
What if I were to cut this cheese in half until I could not make any smaller pieces?
I shall call these uncuttable pieces, atoms.
Sometime in the 5th century BC...
A Greek philosopher named Democritus did a thought experiment.
These atoms probably can't be destroyed either
It wasn't until the late 1700s when the thought of atoms was looked at again.
However, John Dalton's theory did not account for static electricity, until a scientist named Micheal Faraday showed that atoms could gain electric charges.
+
-
But there was still more to discover about the atom. This was proven by JJ Thomson, when he discovered electrons in 1897.
Another physicist named Ernest Rutherford discovered that electrons orbited around a nucleus in the centre of an atom in 1911.
In 1913, a scientist named Niels Bohr claimed that electrons had specific orbits based on a certain amount of energy.
Suddenly, in 1932, a scientist named James Chadwick discovered that the nucleus of an atom didn't just consist of protons, but a neutrally charged particle called a neutron.
And this leaves us with our model of the atom today!
What if I were to cut this cheese in half until I could not make any smaller pieces?
I shall call these uncuttable pieces, atoms.
Sometime in the 5th century BC...
A Greek philosopher named Democritus did a thought experiment.
These atoms probably can't be destroyed either
It wasn't until the late 1700s when the thought of atoms was looked at again.
However, John Dalton's theory did not account for static electricity, until a scientist named Micheal Faraday showed that atoms could gain electric charges.
+
-
But there was still more to discover about the atom. This was proven by JJ Thomson, when he discovered electrons in 1897.
Another physicist named Ernest Rutherford discovered that electrons orbited around a nucleus in the centre of an atom in 1911.
In 1913, a scientist named Niels Bohr claimed that electrons had specific orbits based on a certain amount of energy.
Suddenly, in 1932, a scientist named James Chadwick discovered that the nucleus of an atom didn't just consist of protons, but a neutrally charged particle called a neutron.
And this leaves us with our model of the atom today!
What if I were to cut this cheese in half until I could not make any smaller pieces?
I shall call these uncuttable pieces, atoms.
Sometime in the 5th century BC...
A Greek philosopher named Democritus did a thought experiment.
These atoms probably can't be destroyed either
It wasn't until the late 1700s when the thought of atoms was looked at again.
However, John Dalton's theory did not account for static electricity, until a scientist named Micheal Faraday showed that atoms could gain electric charges.
+
-
But there was still more to discover about the atom. This was proven by JJ Thomson, when he discovered electrons in 1897.
Another physicist named Ernest Rutherford discovered that electrons orbited around a nucleus in the centre of an atom in 1911.
In 1913, a scientist named Niels Bohr claimed that electrons had specific orbits based on a certain amount of energy.
Suddenly, in 1932, a scientist named James Chadwick discovered that the nucleus of an atom didn't just consist of protons, but a neutrally charged particle called a neutron.
And this leaves us with our model of the atom today!
What if I were to cut this cheese in half until I could not make any smaller pieces?
I shall call these uncuttable pieces, atoms.
Sometime in the 5th century BC...
A Greek philosopher named Democritus did a thought experiment.
These atoms probably can't be destroyed either
It wasn't until the late 1700s when the thought of atoms was looked at again.
However, John Dalton's theory did not account for static electricity, until a scientist named Micheal Faraday showed that atoms could gain electric charges.
+
-
But there was still more to discover about the atom. This was proven by JJ Thomson, when he discovered electrons in 1897.
Another physicist named Ernest Rutherford discovered that electrons orbited around a nucleus in the centre of an atom in 1911.
In 1913, a scientist named Niels Bohr claimed that electrons had specific orbits based on a certain amount of energy.
Suddenly, in 1932, a scientist named James Chadwick discovered that the nucleus of an atom didn't just consist of protons, but a neutrally charged particle called a neutron.
And this leaves us with our model of the atom today!
Storyboard Descriere
Storyboard Text
- Sometime in the 5th century BC...
- What if I were to cut this cheese in half until I could not make any smaller pieces?
- I shall call these uncuttable pieces, atoms.
- A Greek philosopher named Democritus did a thought experiment.
- It wasn't until the late 1700s when the thought of atoms was looked at again.
- What if all matter is made of these atoms, each with its own kind, and when these atoms combine, they form compounds.
- These atoms probably can't be destroyed either
- +
- However, John Dalton's theory did not account for static electricity, until a scientist named Micheal Faraday showed that atoms could gain electric charges.
- -
- But there was still more to discover about the atom. This was proven by JJ Thomson, when he discovered electrons in 1897.
- Another physicist named Ernest Rutherford discovered that electrons orbited around a nucleus in the centre of an atom in 1911.
- In 1913, a scientist named Niels Bohr claimed that electrons had specific orbits based on a certain amount of energy.
- And this leaves us with our model of the atom today!
- Suddenly, in 1932, a scientist named James Chadwick discovered that the nucleus of an atom didn't just consist of protons, but a neutrally charged particle called a neutron.


