2 part of cartoon
Storyboard Text
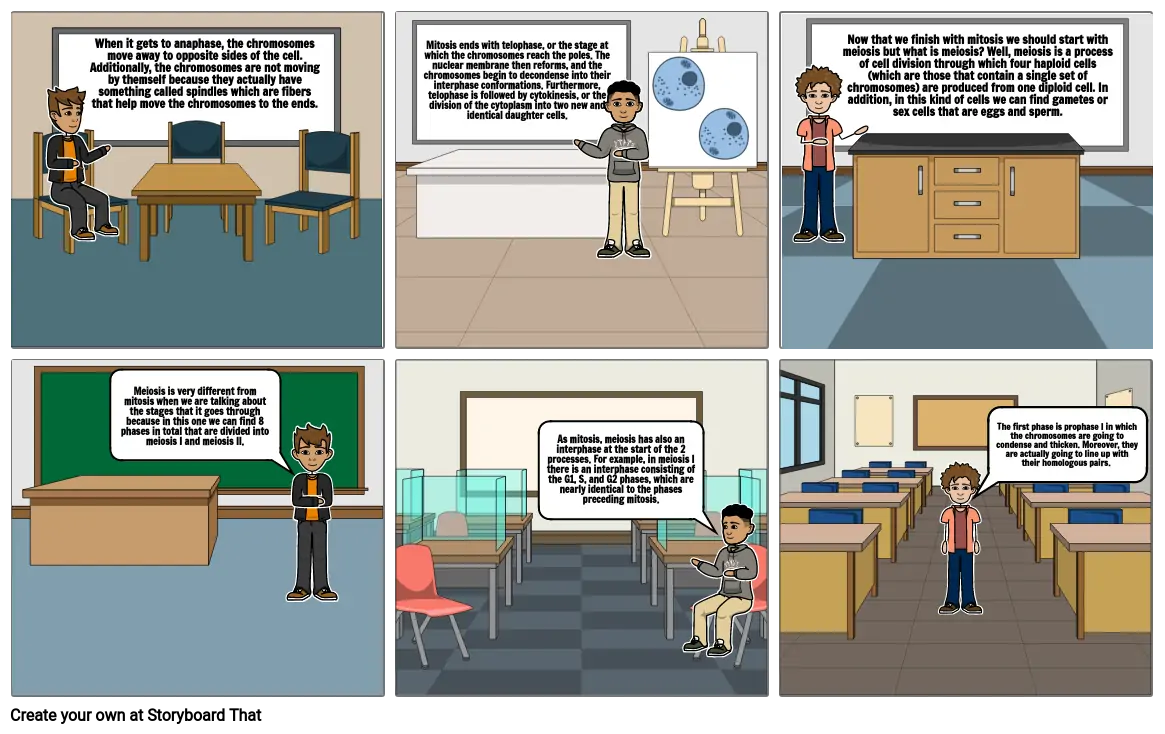
- When it gets to anaphase, the chromosomes move away to opposite sides of the cell. Additionally, the chromosomes are not moving by themself because they actually have something called spindles which are fibers that help move the chromosomes to the ends.
- Mitosis ends with telophase, or the stage at which the chromosomes reach the poles. The nuclear membrane then reforms, and the chromosomes begin to decondense into their interphase conformations. Furthermore, telophase is followed by cytokinesis, or the division of the cytoplasm into two new and identical daughter cells.
- Now that we finish with mitosis we should start with meiosis but what is meiosis? Well, meiosis is a process of cell division through which four haploid cells (which are those that contain a single set of chromosomes) are produced from one diploid cell. In addition, in this kind of cells we can find gametes or sex cells that are eggs and sperm.
- Meiosis is very different from mitosis when we are talking about the stages that it goes through because in this one we can find 8 phases in total that are divided into meiosis I and meiosis II.
- As mitosis, meiosis has also an interphase at the start of the 2 processes. For example, in meiosis I there is an interphase consisting of the G1, S, and G2 phases, which are nearly identical to the phases preceding mitosis.
- The first phase is prophase I in which the chromosomes are going to condense and thicken. Moreover, they are actually going to line up with their homologous pairs.
Peste 30 de milioane de Storyboard-uri create

