chiscakes story
Storyboard Tekst
- Dia: 1
- One day, Aljay visited Chin to her house to suprise her because its her birthday. But when he got to Chin's house, he saw her crying. Because of what he found out, he decided to celebrate Chin's birthday at the Hot Air Balloon Festival.
- Dia: 2
- Aljay and Chin talked about the topic that their teacher discussed in Science subject. Charles’ law, a statement that the volume occupied by a fixed amount of gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature, if the pressure remains constant.
- Dia: 3
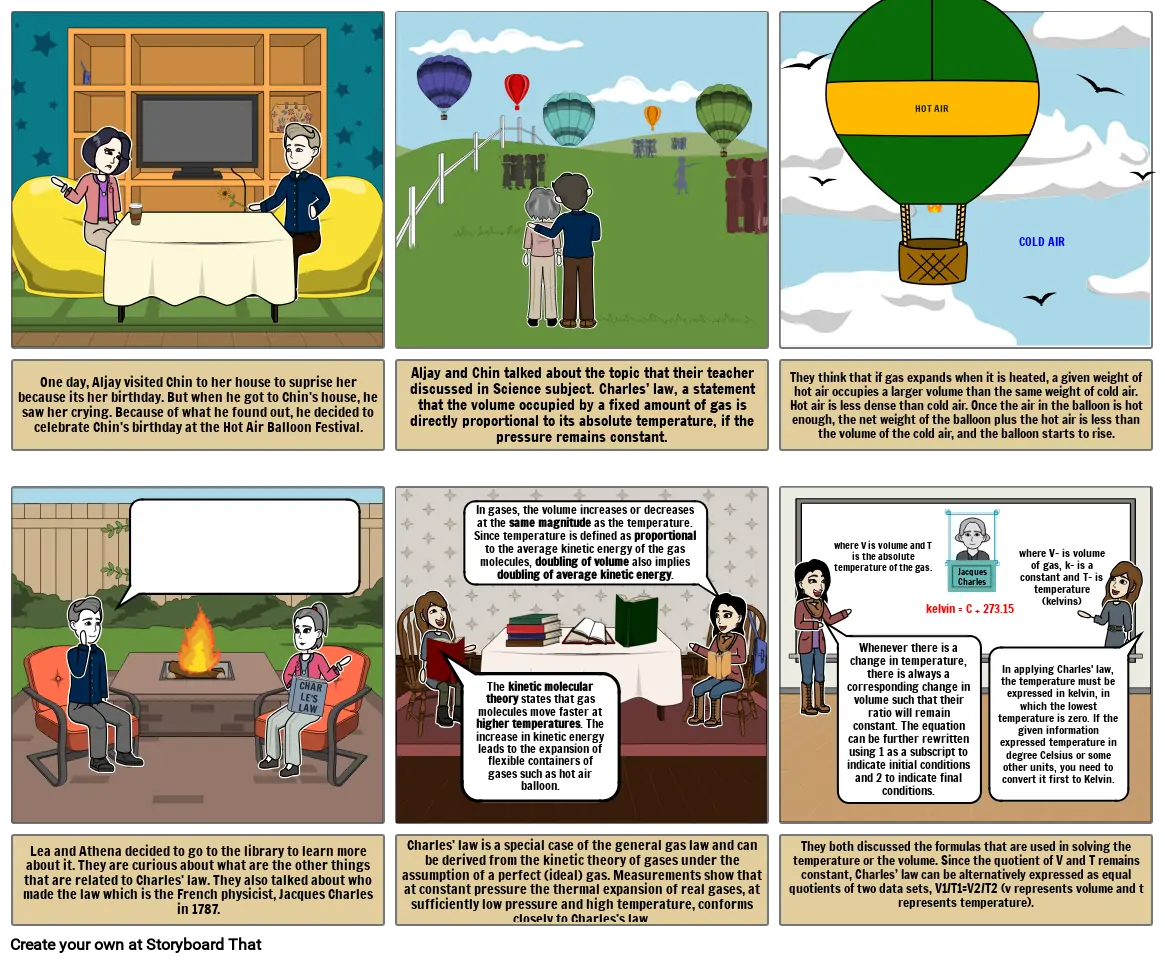
- HOT AIR
- COLD AIR
- They think that if gas expands when it is heated, a given weight of hot air occupies a larger volume than the same weight of cold air. Hot air is less dense than cold air. Once the air in the balloon is hot enough, the net weight of the balloon plus the hot air is less than the volume of the cold air, and the balloon starts to rise.
- Dia: 4
- CHARLE'S LAW
- CHARLE'SLAW
- Lea and Athena decided to go to the library to learn more about it. They are curious about what are the other things that are related to Charles' law. They also talked about who made the law which is the French physicist, Jacques Charles in 1787.
- Dia: 5
- In gases, the volume increases or decreases at the same magnitude as the temperature. Since temperature is defined as proportional to the average kinetic energy of the gas molecules, doubling of volume also implies doubling of average kinetic energy.
- The kinetic molecular theory states that gas molecules move faster at higher temperatures. The increase in kinetic energy leads to the expansion of flexible containers of gases such as hot air balloon.
- Charles' law is a special case of the general gas law and can be derived from the kinetic theory of gases under the assumption of a perfect (ideal) gas. Measurements show that at constant pressure the thermal expansion of real gases, at sufficiently low pressure and high temperature, conforms closely to Charles’s law.
- Dia: 6
-
- where V is volume and T is the absolute temperature of the gas.
- where V- is volume of gas, k- is a constant and T- is temperature (kelvins)
- Jacques Charles
- kelvin = C + 273.15
- Whenever there is a change in temperature, there is always a corresponding change in volume such that their ratio will remain constant. The equation can be further rewritten using 1 as a subscript to indicate initial conditions and 2 to indicate final conditions.
- In applying Charles' law, the temperature must be expressed in kelvin, in which the lowest temperature is zero. If the given information expressed temperature in degree Celsius or some other units, you need to convert it first to Kelvin.
- They both discussed the formulas that are used in solving the temperature or the volume. Since the quotient of V and T remains constant, Charles’ law can be alternatively expressed as equal quotients of two data sets, V1/T1=V2/T2 (v represents volume and t represents temperature).
Meer dan 30 miljoen storyboards gemaakt

