earth science
Siužetinės Linijos Tekstas
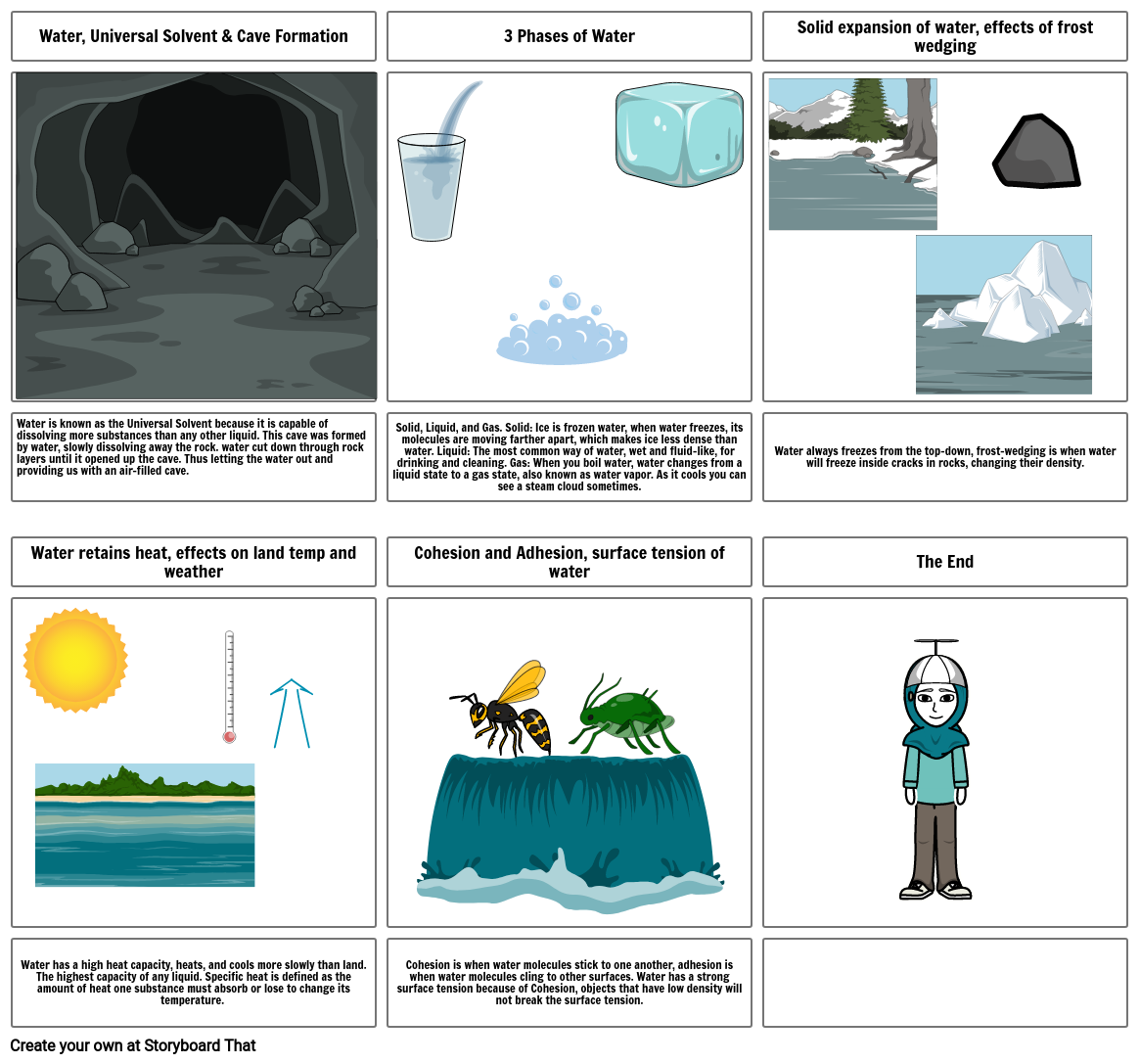
- Water, Universal Solvent & Cave Formation
- 3 Phases of Water
- Solid expansion of water, effects of frost wedging
- Water is known as the Universal Solvent because it is capable of dissolving more substances than any other liquid. This cave was formed by water, slowly dissolving away the rock. water cut down through rock layers until it opened up the cave. Thus letting the water out and providing us with an air-filled cave.
- Water retains heat, effects on land temp and weather
- Solid, Liquid, and Gas. Solid: Ice is frozen water, when water freezes, its molecules are moving farther apart, which makes ice less dense than water. Liquid: The most common way of water, wet and fluid-like, for drinking and cleaning. Gas: When you boil water, water changes from a liquid state to a gas state, also known as water vapor. As it cools you can see a steam cloud sometimes.
- Cohesion and Adhesion, surface tension of water
- Water always freezes from the top-down, frost-wedging is when water will freeze inside cracks in rocks, changing their density.
- The End
- Water has a high heat capacity, heats, and cools more slowly than land. The highest capacity of any liquid. Specific heat is defined as the amount of heat one substance must absorb or lose to change its temperature.
- Cohesion is when water molecules stick to one another, adhesion is when water molecules cling to other surfaces. Water has a strong surface tension because of Cohesion, objects that have low density will not break the surface tension.
-
Sukurta daugiau nei 30 milijonų siužetinių lentelių

