The Geography and Early Development of Rome
Siužetinės Linijos Tekstas
- Location and Geography of Rome
- The Myth of Romulus and Remus
- The Etruscan Influence of Engineering
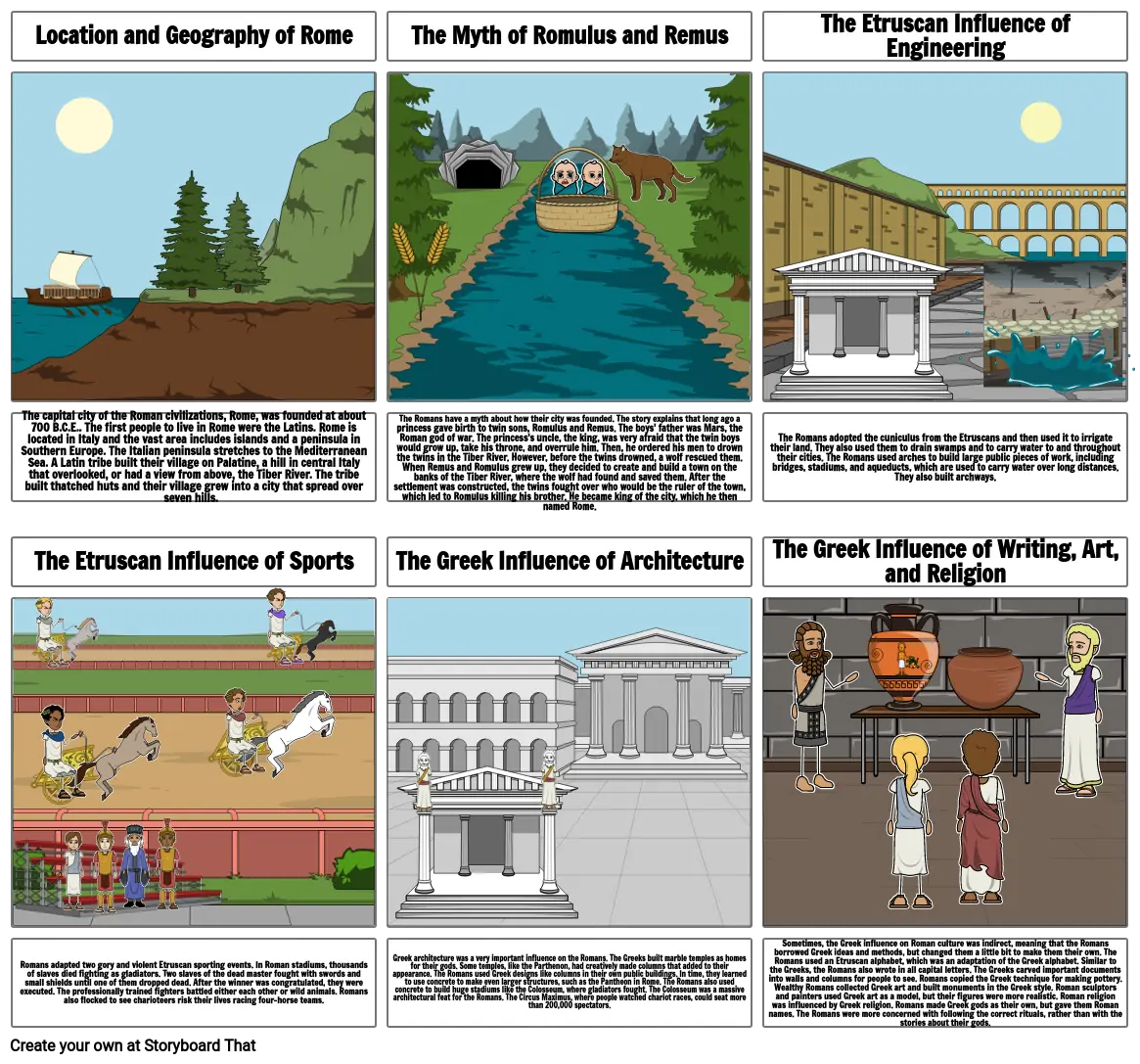
- The capital city of the Roman civilizations, Rome, was founded at about 700 B.C.E.. The first people to live in Rome were the Latins. Rome is located in Italy and the vast area includes islands and a peninsula in Southern Europe. The Italian peninsula stretches to the Mediterranean Sea. A Latin tribe built their village on Palatine, a hill in central Italy that overlooked, or had a view from above, the Tiber River. The tribe built thatched huts and their village grew into a city that spread over seven hills.
- The Etruscan Influence of Sports
- The Romans have a myth about how their city was founded. The story explains that long ago a princess gave birth to twin sons, Romulus and Remus. The boys' father was Mars, the Roman god of war. The princess's uncle, the king, was very afraid that the twin boys would grow up, take his throne, and overrule him. Then, he ordered his men to drown the twins in the Tiber River. However, before the twins drowned, a wolf rescued them. When Remus and Romulus grew up, they decided to create and build a town on the banks of the Tiber River, where the wolf had found and saved them. After the settlement was constructed, the twins fought over who would be the ruler of the town, which led to Romulus killing his brother. He became king of the city, which he then named Rome.
- The Greek Influence of Architecture
- The Romans adopted the cuniculus from the Etruscans and then used it to irrigate their land. They also used them to drain swamps and to carry water to and throughout their cities. The Romans used arches to build large public pieces of work, including bridges, stadiums, and aqueducts, which are used to carry water over long distances. They also built archways.
- The Greek Influence of Writing, Art, and Religion
- Romans adapted two gory and violent Etruscan sporting events. In Roman stadiums, thousands of slaves died fighting as gladiators. Two slaves of the dead master fought with swords and small shields until one of them dropped dead. After the winner was congratulated, they were executed. The professionally trained fighters battled either each other or wild animals. Romans also flocked to see charioteers risk their lives racing four-horse teams.
- Greek architecture was a very important influence on the Romans. The Greeks built marble temples as homes for their gods. Some temples, like the Parthenon, had creatively made columns that added to their appearance. The Romans used Greek designs like columns in their own public buildings. In time, they learned to use concrete to make even larger structures, such as the Pantheon in Rome. The Romans also used concrete to build huge stadiums like the Colosseum, where gladiators fought. The Colosseum was a massive architectural feat for the Romans. The Circus Maximus, where people watched chariot races, could seat more than 200,000 spectators.
- Sometimes, the Greek influence on Roman culture was indirect, meaning that the Romans borrowed Greek ideas and methods, but changed them a little bit to make them their own. The Romans used an Etruscan alphabet, which was an adaptation of the Greek alphabet. Similar to the Greeks, the Romans also wrote in all capital letters. The Greeks carved important documents into walls and columns for people to see. Romans copied the Greek technique for making pottery. Wealthy Romans collected Greek art and built monuments in the Greek style. Roman sculptors and painters used Greek art as a model, but their figures were more realistic. Roman religion was influenced by Greek religion. Romans made Greek gods as their own, but gave them Roman names. The Romans were more concerned with following the correct rituals, rather than with the stories about their gods.
Sukurta daugiau nei 30 milijonų siužetinių lentelių

