BIO YANG KUCINTAI
Siužetinės Linijos Tekstas
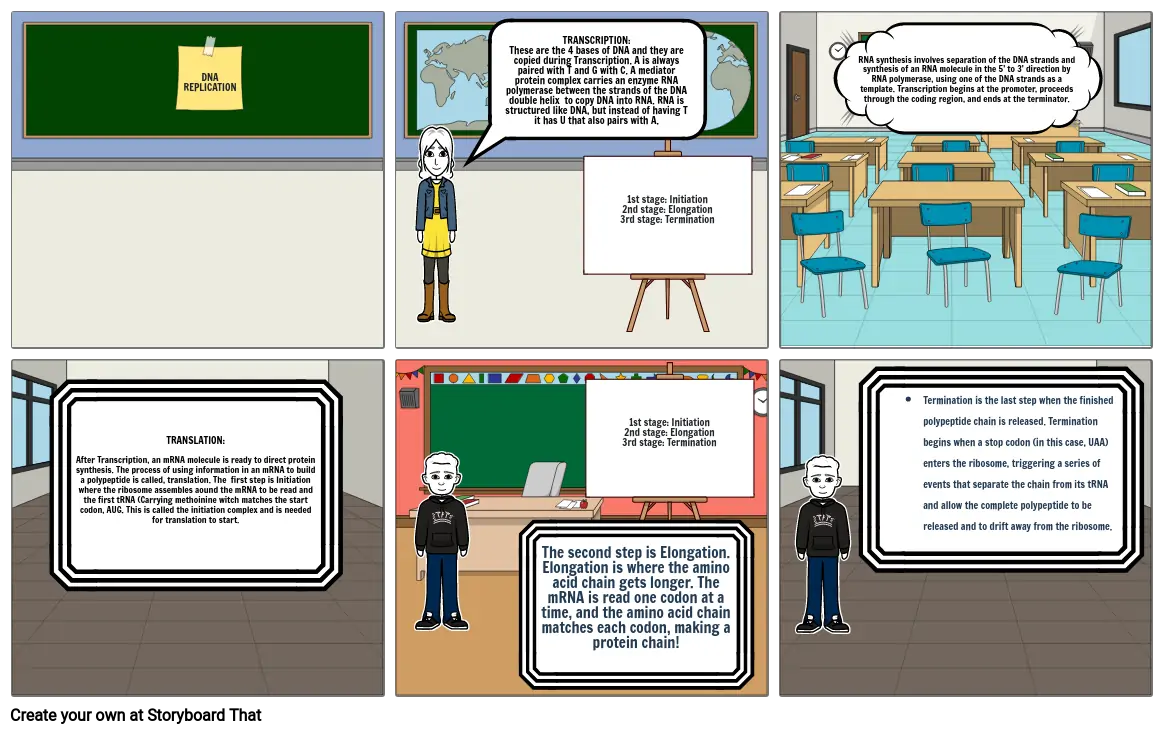
- DNA REPLICATION
- TRANSCRIPTION:These are the 4 bases of DNA and they are copied during Transcription. A is always paired with T and G with C. A mediator protein complex carries an enzyme RNA polymerase between the strands of the DNA double helix to copy DNA into RNA. RNA is structured like DNA, but instead of having T it has U that also pairs with A.
- 1st stage: Initiation2nd stage: Elongation3rd stage: Termination
- RNA synthesis involves separation of the DNA strands and synthesis of an RNA molecule in the 5' to 3' direction by RNA polymerase, using one of the DNA strands as a template. Transcription begins at the promoter, proceeds through the coding region, and ends at the terminator.
- TRANSLATION:After Transcription, an mRNA molecule is ready to direct protein synthesis. The process of using information in an mRNA to build a polypeptide is called, translation. The first step is Initiation where the ribosome assembles aound the mRNA to be read and the first tRNA (Carrying methoinine witch matches the start codon, AUG. This is called the initiation complex and is needed for translation to start.
- The second step is Elongation. Elongation is where the amino acid chain gets longer. The mRNA is read one codon at a time, and the amino acid chain matches each codon, making a protein chain!
- 1st stage: Initiation2nd stage: Elongation3rd stage: Termination
- Termination is the last step when the finished polypeptide chain is released. Termination begins when a stop codon (in this case, UAA) enters the ribosome, triggering a series of events that separate the chain from its tRNA and allow the complete polypeptide to be released and to drift away from the ribosome.
Sukurta daugiau nei 30 milijonų siužetinių lentelių

