Unknown Story
Siužetinės Linijos Tekstas
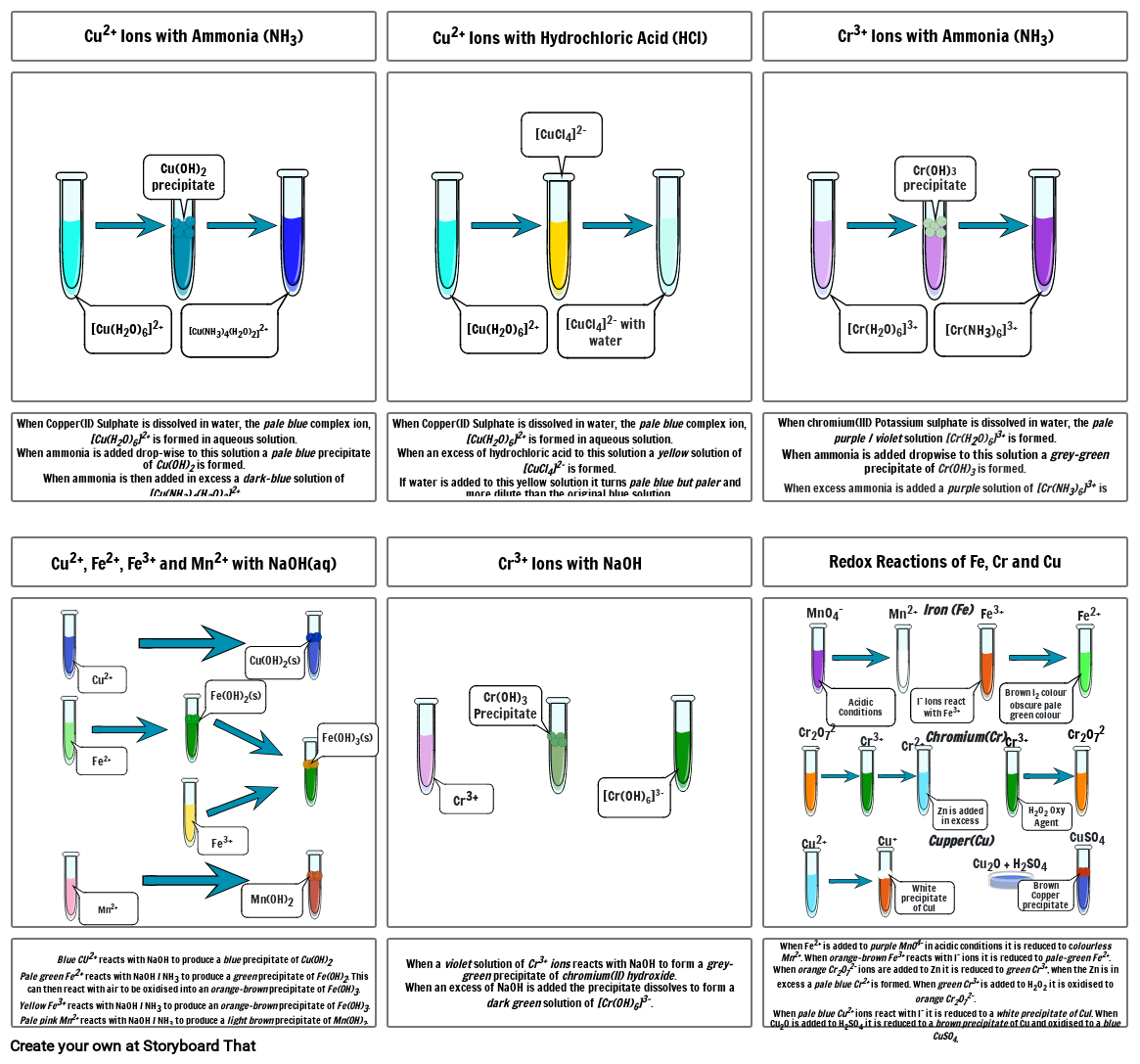
- Cu2+ Ions with Ammonia (NH3)
- [Cu(H20)6]2+
- Cu(OH)2 precipitate
- [Cu(NH3)4(H20)2]2+
- Cu2+ Ions with Hydrochloric Acid (HCl)
- [Cu(H20)6]2+
- [CuCl4]2-
- [CuCl4]2- with water
- Cr3+ Ions with Ammonia (NH3)
- [Cr(H20)6]3+
- Cr(OH)3 precipitate
- [Cr(NH3)6]3+
- When Copper(II) Sulphate is dissolved in water, the pale blue complex ion, [Cu(H20)6]2+ is formed in aqueous solution.When ammonia is added drop-wise to this solution a pale blue precipitate of Cu(OH)2 is formed.When ammonia is then added in excess a dark-blue solution of [Cu(NH3)4(H20)2]2+
- Cu2+, Fe2+, Fe3+ and Mn2+ with NaOH(aq)
- Cu2+
- Fe(OH)2(s)
- Cu(OH)2(s)
- When Copper(II) Sulphate is dissolved in water, the pale blue complex ion, [Cu(H20)6]2+ is formed in aqueous solution.When an excess of hydrochloric acid to this solution a yellow solution of [CuCl4]2- is formed.If water is added to this yellow solution it turns pale blue but paler and more dilute than the original blue solution.
- Cr3+ Ions with NaOH
- When chromium(III) Potassium sulphate is dissolved in water, the pale purple / violet solution [Cr(H20)6]3+ is formed.When ammonia is added dropwise to this solution a grey-green precipitate of Cr(OH)3 is formed. When excess ammonia is added a purple solution of [Cr(NH3)6]3+ is formed.
- Redox Reactions of Fe, Cr and Cu
- MnO4-
- Acidic Conditions
- Mn2+
- I- Ions react with Fe3+
- Iron (Fe)
- Fe3+
- Brown I2 colour obscure pale green colour
- Fe2+
- Blue CU2+ reacts with NaOH to produce a blue precipitate of Cu(OH)2Pale green Fe2+ reacts with NaOH / NH3 to produce a green precipitate of Fe(OH)2. This can then react with air to be oxidised into an orange-brown precipitate of Fe(OH)3.Yellow Fe3+ reacts with NaOH / NH3 to produce an orange-brown precipitate of Fe(OH)3.Pale pink Mn2+ reacts with NaOH / NH3 to produce a light brown precipitate of Mn(OH)2.
- Fe2+
- Mn2+
- Fe3+
- Mn(OH)2
- Fe(OH)3(s)
- When a violet solution of Cr3+ ions reacts with NaOH to form a grey-green precipitate of chromium(II) hydroxide. When an excess of NaOH is added the precipitate dissolves to form a dark green solution of [Cr(OH)6]3-.
- Cr3+
- Cr(OH)3Precipitate
- [Cr(OH)6]3-
- When Fe2+ is added to purple MnO4- in acidic conditions it is reduced to colourless Mn2+. When orange-brown Fe3+ reacts with I- ions it is reduced to pale-green Fe2+.When orange Cr2O72- ions are added to Zn it is reduced to green Cr3+, when the Zn is in excess a pale blue Cr2+ is formed. When green Cr3+ is added to H2O2 it is oxidised to orange Cr2O72-. When pale blue Cu2+ ions react with I- it is reduced to a white precipitate of CuI. When Cu2O is added to H2SO4 it is reduced to a brown precipitate of Cu and oxidised to a blue CuSO4.
- Cu2+
- Cr2O72-
- Cr3+
- Cu+
- White precipitate of CuI
- Cr2+
- Cupper(Cu)
- Chromium(Cr)
- Zn is added in excess
- Cu2O + H2SO4
- Cr3+
- H2O2 Oxy Agent
- Brown Copper precipitate
- Cr2O72-
- CuSO4
Sukurta daugiau nei 30 milijonų siužetinių lentelių

