No sickness seen with the COVID vaccine!
Siužetinės Linijos Tekstas
- Cellular Respiration
- We need cellular respiration to survive. It provides us with energy needed to function! There is an equation for every step, but the equation for the cycle is... C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6 O 2 -- 6 CO 2 + 6 H 2 O + ATP
- Step #1- GlycosisC6H12O6 + 2ATP ---- 2 pyruvate + 4 ATP + 2H2O Step #2- Pyruvate Oxidation2 pyruvate-- 2Acetyl- CoA+2NADH Step #3- Krebs Cycle2Acetyl-CoA-- 2 ATP+ 6NADH+2FADH Step #4- Electron Transport Chain10 NADH + 2 FADH2 +6 O2 --6 H2O+ 34 ATP Complete Equation:C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6 O 2 -- 6 CO 2 + 6 H 2 O + ATP
- Process broken down
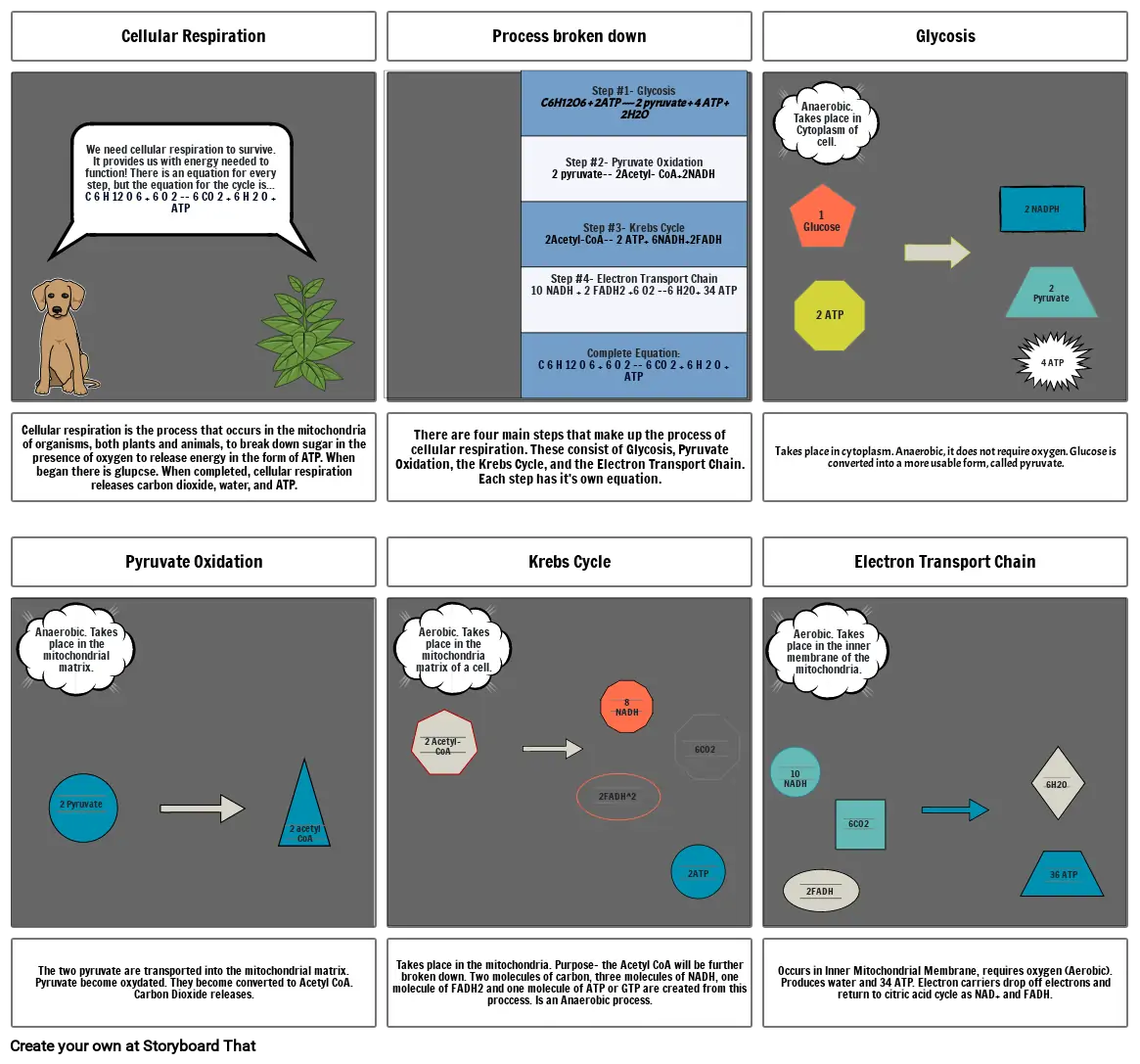
- Glycosis
- Anaerobic. Takes place in Cytoplasm of cell.
- 1 Glucose
- 2 ATP
- 2 NADPH
- 2 Pyruvate
- 4 ATP
- Cellular respiration is the process that occurs in the mitochondria of organisms, both plants and animals, to break down sugar in the presence of oxygen to release energy in the form of ATP. When began there is glupcse. When completed, cellular respiration releases carbon dioxide, water, and ATP.
- Pyruvate Oxidation
- Anaerobic. Takes place in the mitochondrial matrix.
- There are four main steps that make up the process of cellular respiration. These consist of Glycosis, Pyruvate Oxidation, the Krebs Cycle, and the Electron Transport Chain. Each step has it's own equation.
- Krebs Cycle
- Aerobic. Takes place in the mitochondria matrix of a cell.
- Takes place in cytoplasm. Anaerobic, it does not require oxygen. Glucose is converted into a more usable form, called pyruvate.
- Electron Transport Chain
- Aerobic. Takes place in the inner membrane of the mitochondria.
- The two pyruvate are transported into the mitochondrial matrix. Pyruvate become oxydated. They become converted to Acetyl CoA. Carbon Dioxide releases.
- 2 Pyruvate
- 2 acetyl CoA
- Takes place in the mitochondria. Purpose- the Acetyl CoA will be further broken down. Two molecules of carbon, three molecules of NADH, one molecule of FADH2 and one molecule of ATP or GTP are created from this proccess. Is an Anaerobic process.
- 2 Acetyl-CoA
- 2FADH^2
- 8 NADH
- 2ATP
- 6CO2
- Occurs in Inner Mitochondrial Membrane, requires oxygen (Aerobic). Produces water and 34 ATP. Electron carriers drop off electrons and return to citric acid cycle as NAD+ and FADH.
- 10 NADH
- 2FADH
- 6CO2
- 6H2O
- 36 ATP
Sukurta daugiau nei 30 milijonų siužetinių lentelių

