ENERGY FLOW WITHIN THE CELL
Siužetinės Linijos Tekstas
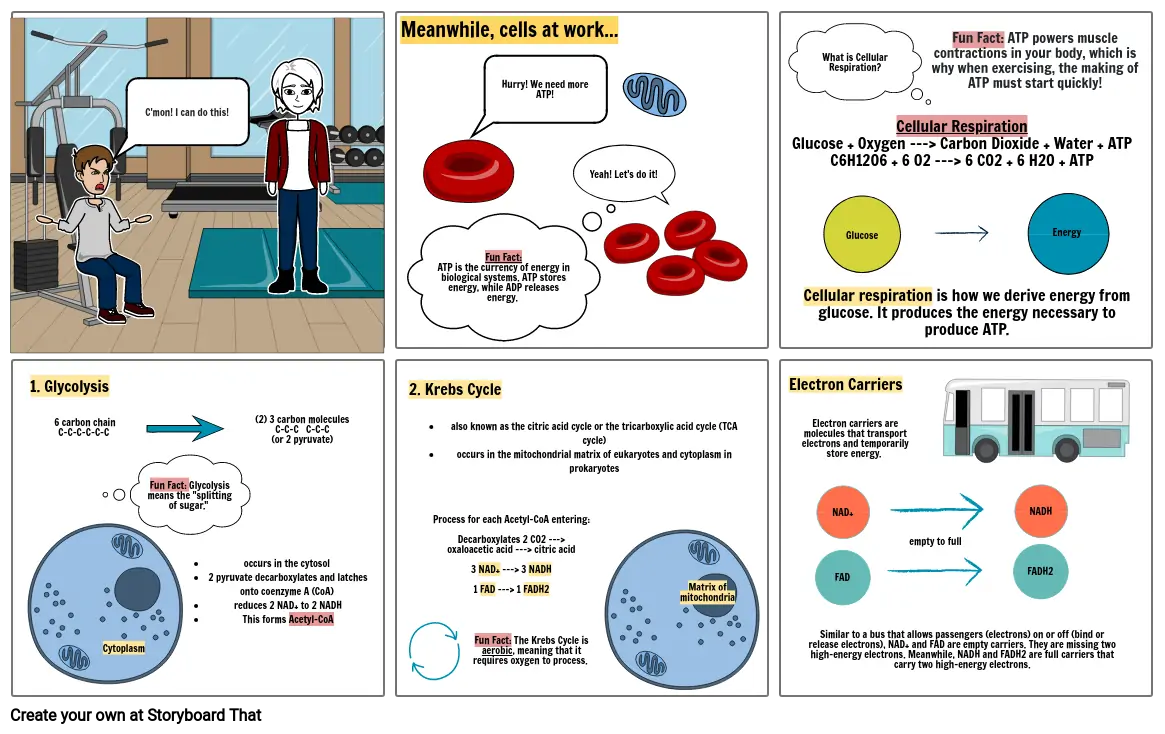
- C'mon! I can do this!
- Meanwhile, cells at work...
- Fun Fact:ATP is the currency of energy in biological systems. ATP stores energy, while ADP releases energy.
- Hurry! We need more ATP!
- Yeah! Let's do it!
- What is Cellular Respiration?
- Cellular RespirationGlucose + Oxygen ---> Carbon Dioxide + Water + ATPC6H12O6 + 6 O2 ---> 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + ATP
- Cellular respiration is how we derive energy from glucose. It produces the energy necessary to produce ATP.
- Glucose
- Fun Fact: ATP powers musclecontractions in your body, which is why when exercising, the making of ATP must start quickly!
- Energy
- 1. Glycolysis
- 6 carbon chainC-C-C-C-C-C
- Cytoplasm
- Fun Fact: Glycolysis means the "splitting of sugar."
- occurs in the cytosol 2 pyruvate decarboxylates and latches onto coenzyme A (CoA) reduces 2 NAD+ to 2 NADHThis forms Acetyl-CoA
- (2) 3 carbon moleculesC-C-C C-C-C(or 2 pyruvate)
- 2. Krebs Cycle
- also known as the citric acid cycle or the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle)occurs in the mitochondrial matrix of eukaryotes and cytoplasm in prokaryotes
- Process for each Acetyl-CoA entering:Decarboxylates 2 CO2 ---> oxaloacetic acid ---> citric acid3 NAD+ ---> 3 NADH1 FAD ---> 1 FADH2
- Fun Fact: The Krebs Cycle is aerobic, meaning that it requires oxygen to process.
- Matrix of mitochondria
- Electron Carriers
- Electron carriers are molecules that transport electrons and temporarily store energy.
- Similar to a bus that allows passengers (electrons) on or off (bind or release electrons), NAD+ and FAD are empty carriers. They are missing two high-energy electrons. Meanwhile, NADH and FADH2 are full carriers that carry two high-energy electrons.
- FAD
- NAD+
- empty to full
- FADH2
- NADH
Sukurta daugiau nei 30 milijonų siužetinių lentelių

