11 GAS-3 Sayson, Alex Joseph N. Comic Strip
Siužetinės Linijos Tekstas
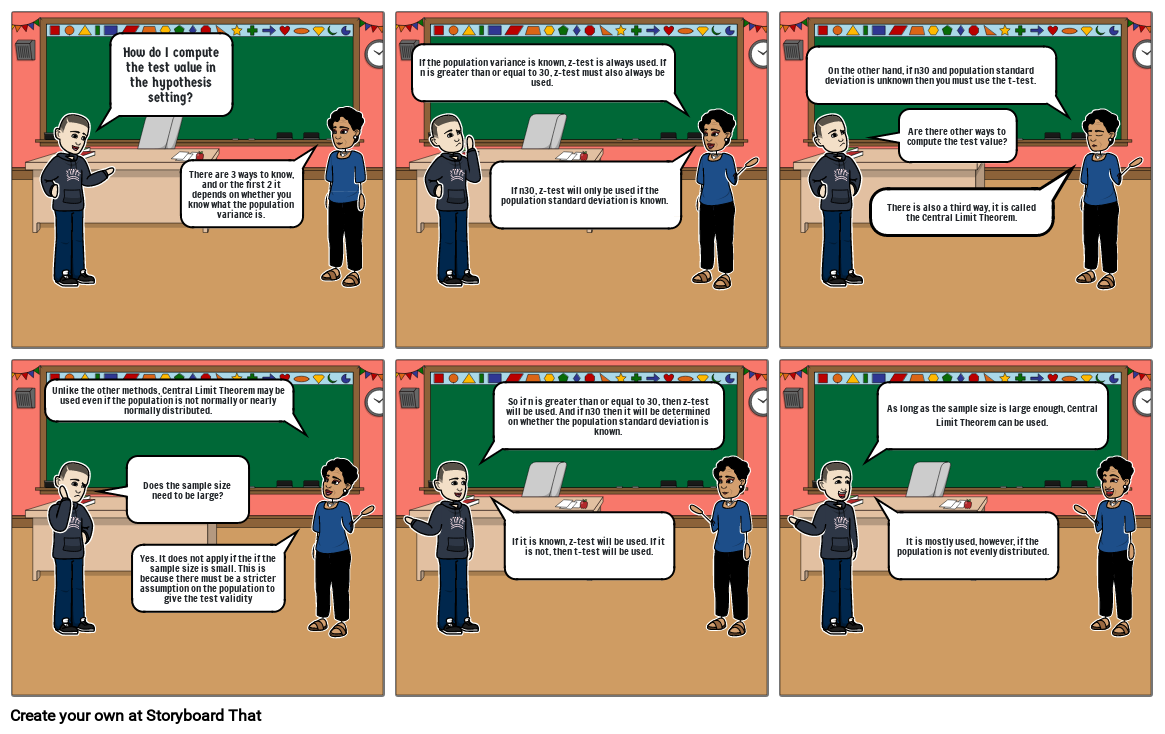
- How do I compute the test value in the hypothesis setting?
- There are 3 ways to know, and or the first 2 it depends on whether you know what the population variance is.
- If the population variance is known, z-test is always used. If n is greater than or equal to 30, z-test must also always be used.
- If n30, z-test will only be used if the population standard deviation is known.
- On the other hand, if n30 and population standard deviation is unknown then you must use the t-test.
- Are there other ways to compute the test value?
- There is also a third way, it is called the Central Limit Theorem.
- Unlike the other methods, Central Limit Theorem may be used even if the population is not normally or nearly normally distributed.
- Does the sample size need to be large?
- Yes. It does not apply if the if the sample size is small. This is because there must be a stricter assumption on the population to give the test validity
- So if n is greater than or equal to 30, then z-test will be used. And if n30 then it will be determined on whether the population standard deviation is known.
- If it is known, z-test will be used. If it is not, then t-test will be used.
- As long as the sample size is large enough, Central Limit Theorem can be used.
- It is mostly used, however, if the population is not evenly distributed.
Sukurta daugiau nei 30 milijonų siužetinių lentelių

