Atomic History Timeline
Testo Storyboard
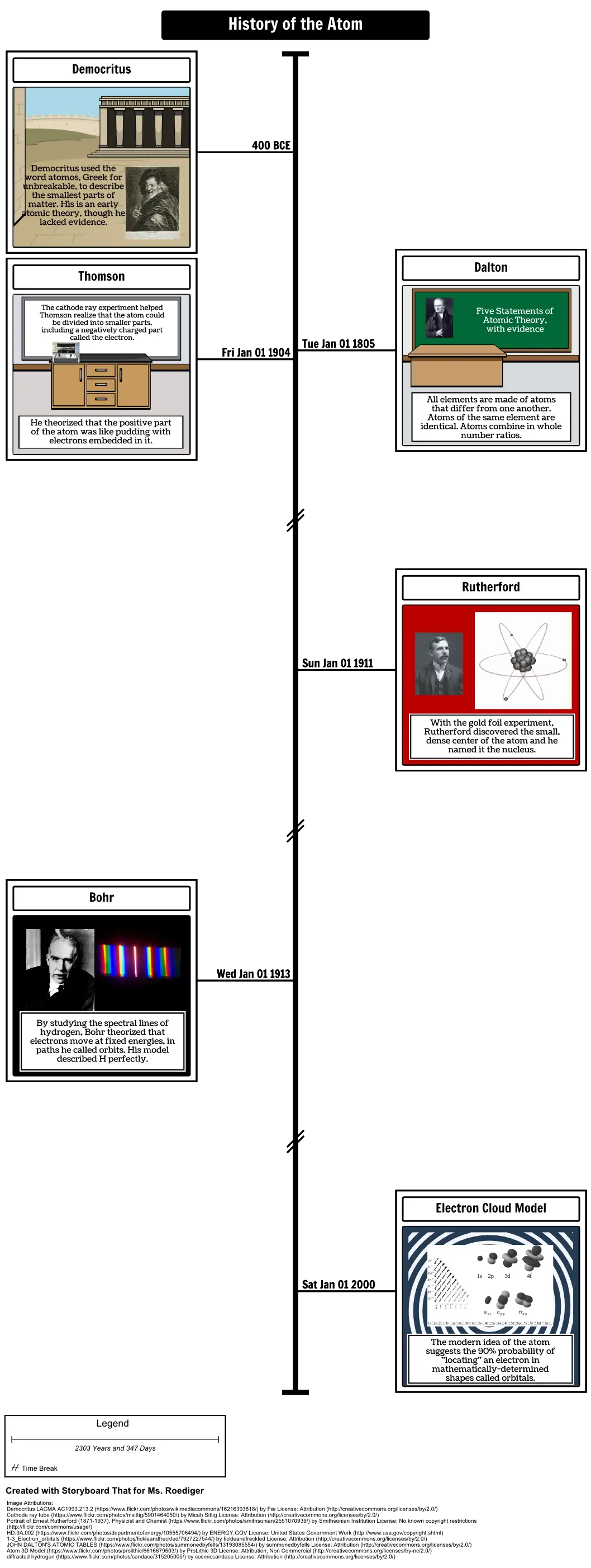
- Democritus
- Democritus used the word atomos, Greek for unbreakable, to describe the smallest parts of matter. His is an early atomic theory, though he lacked evidence.
- History of the Atom
- Thomson
- The cathode ray experiment helped Thomson realize that the atom could be divided into smaller parts, including a negatively charged part called the electron.
- Dalton
- Five Statements of Atomic Theory, with evidence
- He theorized that the positive part of the atom was like pudding with electrons embedded in it.
- All elements are made of atoms that differ from one another. Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms combine in whole number ratios.
- Rutherford
- With the gold foil experiment, Rutherford discovered the small, dense center of the atom and he named it the nucleus.
- Bohr
- By studying the spectral lines of hydrogen, Bohr theorized that electrons move at fixed energies, in paths he called orbits. His model described H perfectly.
- Electron Cloud Model
- The modern idea of the atom suggests the 90% probability of "locating" an electron in mathematically-determined shapes called orbitals.
Attribuzioni Immagine
- 1-3_Electron_orbitals - fickleandfreckled - (Licenza Attribution )
- Atom 3D Model - ProLithic 3D - (Licenza Attribution, Non Commercial )
- Cathode ray tube - Micah Sittig - (Licenza Attribution )
- Democritus LACMA AC1993.213.2 - Fæ - (Licenza Attribution )
- diffracted hydrogen - cosmiccandace - (Licenza Attribution )
- HD.3A.002 - ENERGY.GOV - (Licenza United States Government Work )
- JOHN DALTON'S ATOMIC TABLES - summonedbyfells - (Licenza Attribution )
- Portrait of Ernest Rutherford (1871-1937), Physicist and Chemist - Smithsonian Institution - (Licenza No known copyright restrictions )
Oltre 30 milioni di storyboard creati
Nessun Download, Nessuna Carta di Credito e Nessun Accesso Necessario per Provare!
