how a bill becomes a law by Hannah Lilly and Noelle Munoz
Testo Storyboard
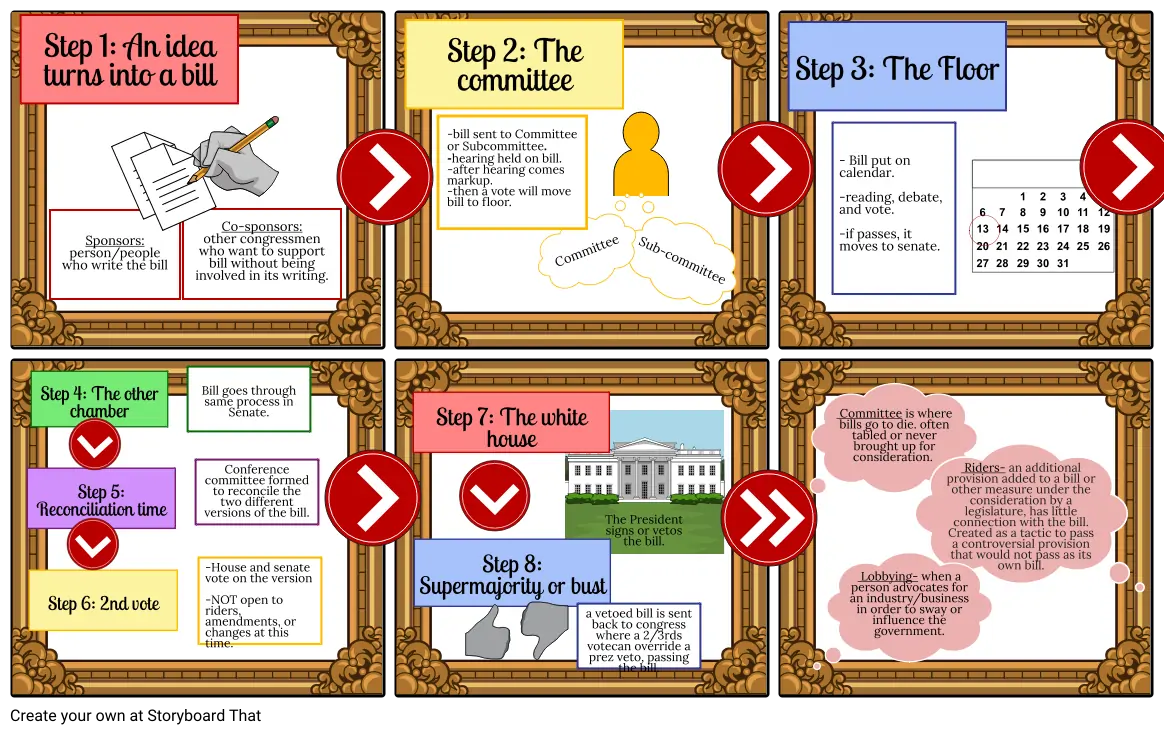
- Step 1: An idea turns into a bill
- Sponsors: person/people who write the bill
- Co-sponsors: other congressmen who want to support bill without being involved in its writing.
- Step 2: The committee
- -bill sent to Committee or Subcommittee. -hearing held on bill. -after hearing comes markup. -then a vote will move bill to floor.
- Committee
- Sub-committee
- Step 3: The Floor
- - Bill put on calendar. -reading, debate, and vote. -if passes, it moves to senate.
- Step 5: Reconciliation time
- Step 6: 2nd vote
- Step 4: The other chamber
- Bill goes through same process in Senate.
- Conference committee formed to reconcile the two different versions of the bill.
- -House and senate vote on the version -NOT open to riders, amendments, or changes at this time.
- Step 7: The white house
- Step 8: Supermajority or bust
- a vetoed bill is sent back to congress where a 2/3rds votecan override a prez veto, passing the bill.
- The President signs or vetos the bill.
- Committee is where bills go to die. often tabled or never brought up for consideration.
- Lobbying- when a person advocates for an industry/business in order to sway or influence the government.
- Riders- an additional provision added to a bill or other measure under the consideration by a legislature, has little connection with the bill. Created as a tactic to pass a controversial provision that would not pass as its own bill.
Oltre 30 milioni di storyboard creati

