remodeling
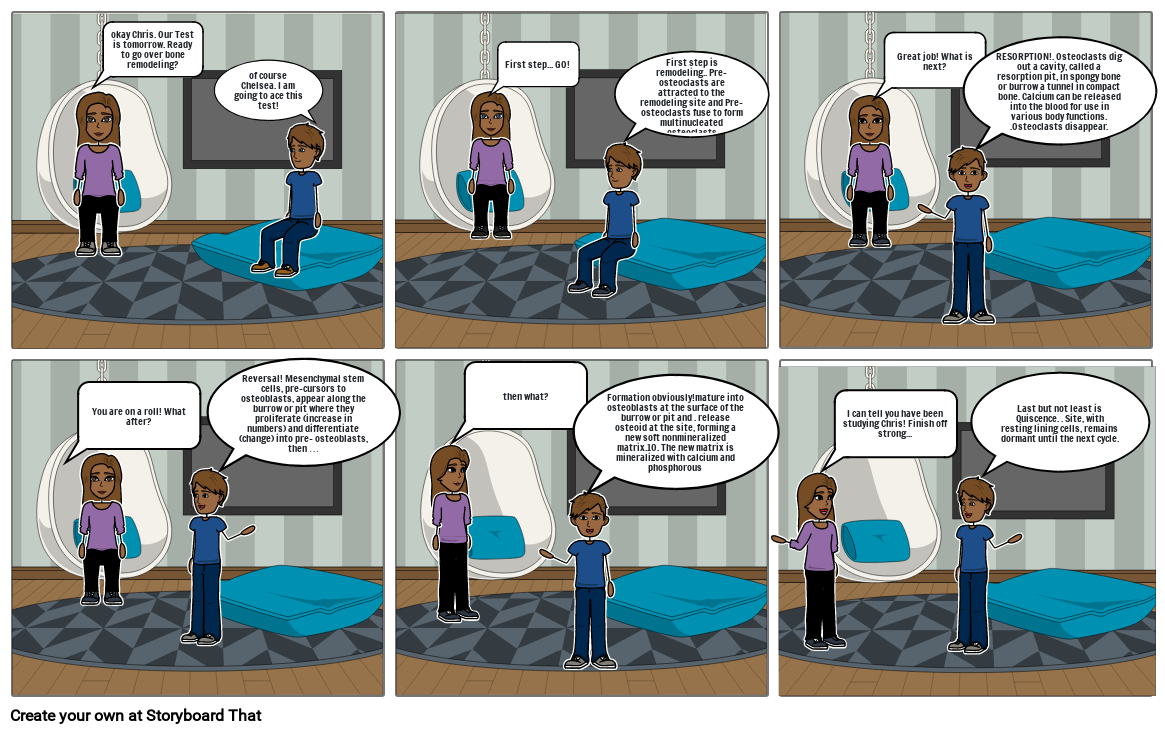
okay Chris. Our Test is tomorrow. Ready to go over bone remodeling?
of course Chelsea. I am going to ace this test!
First step... GO!
First step is remodeling.. Pre-osteoclasts are attracted to the remodeling site and Pre-osteoclasts fuse to form multinucleated osteoclasts
Great job! What is next?
RESORPTION!. Osteoclasts dig out a cavity, called a resorption pit, in spongy bone or burrow a tunnel in compact bone. Calcium can be released into the blood for use in various body functions. .Osteoclasts disappear.
You are on a roll! What after?
Reversal! Mesenchymal stem cells, pre-cursors to osteoblasts, appear along the burrow or pit where they proliferate (increase in numbers) and differentiate (change) into pre- osteoblasts, then …
then what?
Formation obviously!mature into osteoblasts at the surface of the burrow or pit and . release osteoid at the site, forming a new soft nonmineralized matrix.10. The new matrix is mineralized with calcium and phosphorous
I can tell you have been studying Chris! Finish off strong...
Last but not least is Quiscence. . Site, with resting lining cells, remains dormant until the next cycle.
okay Chris. Our Test is tomorrow. Ready to go over bone remodeling?
of course Chelsea. I am going to ace this test!
First step... GO!
First step is remodeling.. Pre-osteoclasts are attracted to the remodeling site and Pre-osteoclasts fuse to form multinucleated osteoclasts
Great job! What is next?
RESORPTION!. Osteoclasts dig out a cavity, called a resorption pit, in spongy bone or burrow a tunnel in compact bone. Calcium can be released into the blood for use in various body functions. .Osteoclasts disappear.
You are on a roll! What after?
Reversal! Mesenchymal stem cells, pre-cursors to osteoblasts, appear along the burrow or pit where they proliferate (increase in numbers) and differentiate (change) into pre- osteoblasts, then …
then what?
Formation obviously!mature into osteoblasts at the surface of the burrow or pit and . release osteoid at the site, forming a new soft nonmineralized matrix.10. The new matrix is mineralized with calcium and phosphorous
I can tell you have been studying Chris! Finish off strong...
Last but not least is Quiscence. . Site, with resting lining cells, remains dormant until the next cycle.
okay Chris. Our Test is tomorrow. Ready to go over bone remodeling?
of course Chelsea. I am going to ace this test!
First step... GO!
First step is remodeling.. Pre-osteoclasts are attracted to the remodeling site and Pre-osteoclasts fuse to form multinucleated osteoclasts
Great job! What is next?
RESORPTION!. Osteoclasts dig out a cavity, called a resorption pit, in spongy bone or burrow a tunnel in compact bone. Calcium can be released into the blood for use in various body functions. .Osteoclasts disappear.
You are on a roll! What after?
Reversal! Mesenchymal stem cells, pre-cursors to osteoblasts, appear along the burrow or pit where they proliferate (increase in numbers) and differentiate (change) into pre- osteoblasts, then …
then what?
Formation obviously!mature into osteoblasts at the surface of the burrow or pit and . release osteoid at the site, forming a new soft nonmineralized matrix.10. The new matrix is mineralized with calcium and phosphorous
I can tell you have been studying Chris! Finish off strong...
Last but not least is Quiscence. . Site, with resting lining cells, remains dormant until the next cycle.
okay Chris. Our Test is tomorrow. Ready to go over bone remodeling?
of course Chelsea. I am going to ace this test!
First step... GO!
First step is remodeling.. Pre-osteoclasts are attracted to the remodeling site and Pre-osteoclasts fuse to form multinucleated osteoclasts
Great job! What is next?
RESORPTION!. Osteoclasts dig out a cavity, called a resorption pit, in spongy bone or burrow a tunnel in compact bone. Calcium can be released into the blood for use in various body functions. .Osteoclasts disappear.
You are on a roll! What after?
Reversal! Mesenchymal stem cells, pre-cursors to osteoblasts, appear along the burrow or pit where they proliferate (increase in numbers) and differentiate (change) into pre- osteoblasts, then …
then what?
Formation obviously!mature into osteoblasts at the surface of the burrow or pit and . release osteoid at the site, forming a new soft nonmineralized matrix.10. The new matrix is mineralized with calcium and phosphorous
I can tell you have been studying Chris! Finish off strong...
Last but not least is Quiscence. . Site, with resting lining cells, remains dormant until the next cycle.
okay Chris. Our Test is tomorrow. Ready to go over bone remodeling?
of course Chelsea. I am going to ace this test!
First step... GO!
First step is remodeling.. Pre-osteoclasts are attracted to the remodeling site and Pre-osteoclasts fuse to form multinucleated osteoclasts
Great job! What is next?
RESORPTION!. Osteoclasts dig out a cavity, called a resorption pit, in spongy bone or burrow a tunnel in compact bone. Calcium can be released into the blood for use in various body functions. .Osteoclasts disappear.
You are on a roll! What after?
Reversal! Mesenchymal stem cells, pre-cursors to osteoblasts, appear along the burrow or pit where they proliferate (increase in numbers) and differentiate (change) into pre- osteoblasts, then …
then what?
Formation obviously!mature into osteoblasts at the surface of the burrow or pit and . release osteoid at the site, forming a new soft nonmineralized matrix.10. The new matrix is mineralized with calcium and phosphorous
I can tell you have been studying Chris! Finish off strong...
Last but not least is Quiscence. . Site, with resting lining cells, remains dormant until the next cycle.
okay Chris. Our Test is tomorrow. Ready to go over bone remodeling?
of course Chelsea. I am going to ace this test!
First step... GO!
First step is remodeling.. Pre-osteoclasts are attracted to the remodeling site and Pre-osteoclasts fuse to form multinucleated osteoclasts
Great job! What is next?
RESORPTION!. Osteoclasts dig out a cavity, called a resorption pit, in spongy bone or burrow a tunnel in compact bone. Calcium can be released into the blood for use in various body functions. .Osteoclasts disappear.
You are on a roll! What after?
Reversal! Mesenchymal stem cells, pre-cursors to osteoblasts, appear along the burrow or pit where they proliferate (increase in numbers) and differentiate (change) into pre- osteoblasts, then …
then what?
Formation obviously!mature into osteoblasts at the surface of the burrow or pit and . release osteoid at the site, forming a new soft nonmineralized matrix.10. The new matrix is mineralized with calcium and phosphorous
I can tell you have been studying Chris! Finish off strong...
Last but not least is Quiscence. . Site, with resting lining cells, remains dormant until the next cycle.
okay Chris. Our Test is tomorrow. Ready to go over bone remodeling?
of course Chelsea. I am going to ace this test!
First step... GO!
First step is remodeling.. Pre-osteoclasts are attracted to the remodeling site and Pre-osteoclasts fuse to form multinucleated osteoclasts
Great job! What is next?
RESORPTION!. Osteoclasts dig out a cavity, called a resorption pit, in spongy bone or burrow a tunnel in compact bone. Calcium can be released into the blood for use in various body functions. .Osteoclasts disappear.
You are on a roll! What after?
Reversal! Mesenchymal stem cells, pre-cursors to osteoblasts, appear along the burrow or pit where they proliferate (increase in numbers) and differentiate (change) into pre- osteoblasts, then …
then what?
Formation obviously!mature into osteoblasts at the surface of the burrow or pit and . release osteoid at the site, forming a new soft nonmineralized matrix.10. The new matrix is mineralized with calcium and phosphorous
I can tell you have been studying Chris! Finish off strong...
Last but not least is Quiscence. . Site, with resting lining cells, remains dormant until the next cycle.
Storyboard Tekst
- okay Chris. Our Test is tomorrow. Ready to go over bone remodeling?
- of course Chelsea. I am going to ace this test!
- First step... GO!
- First step is remodeling.. Pre-osteoclasts are attracted to the remodeling site and Pre-osteoclasts fuse to form multinucleated osteoclasts
- Great job! What is next?
- RESORPTION!. Osteoclasts dig out a cavity, called a resorption pit, in spongy bone or burrow a tunnel in compact bone. Calcium can be released into the blood for use in various body functions. .Osteoclasts disappear.
- You are on a roll! What after?
- Reversal! Mesenchymal stem cells, pre-cursors to osteoblasts, appear along the burrow or pit where they proliferate (increase in numbers) and differentiate (change) into pre- osteoblasts, then …
- then what?
- Formation obviously!mature into osteoblasts at the surface of the burrow or pit and . release osteoid at the site, forming a new soft nonmineralized matrix.10. The new matrix is mineralized with calcium and phosphorous
- I can tell you have been studying Chris! Finish off strong...
- Last but not least is Quiscence. . Site, with resting lining cells, remains dormant until the next cycle.


