Unknown Story
Texte du Storyboard
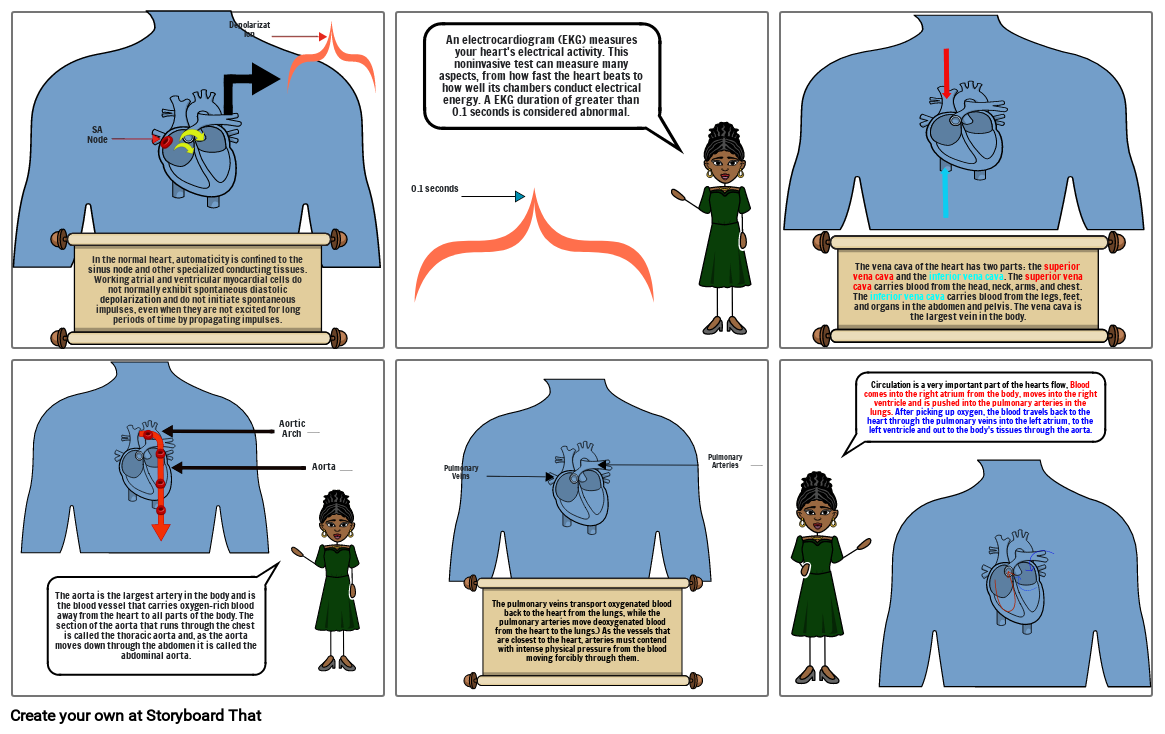
- In the normal heart, automaticity is confined to the sinus node and other specialized conducting tissues. Working atrial and ventricular myocardial cells do not normally exhibit spontaneous diastolic depolarization and do not initiate spontaneous impulses, even when they are not excited for long periods of time by propagating impulses.
- SA Node
- Depolarization
- 0.1 seconds
- An electrocardiogram (EKG) measures your heart's electrical activity. This noninvasive test can measure many aspects, from how fast the heart beats to how well its chambers conduct electrical energy. A EKG duration of greater than 0.1 seconds is considered abnormal.
- The vena cava of the heart has two parts: the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava. The superior vena cava carries blood from the head, neck, arms, and chest. The inferior vena cava carries blood from the legs, feet, and organs in the abdomen and pelvis. The vena cava is the largest vein in the body.
- The aorta is the largest artery in the body and is the blood vessel that carries oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to all parts of the body. The section of the aorta that runs through the chest is called the thoracic aorta and, as the aorta moves down through the abdomen it is called the abdominal aorta.
- Aortic Arch
- Aorta
- Pulmonary Veins
- The pulmonary veins transport oxygenated blood back to the heart from the lungs, while the pulmonary arteries move deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs.) As the vessels that are closest to the heart, arteries must contend with intense physical pressure from the blood moving forcibly through them.
- Pulmonary Arteries
- Circulation is a very important part of the hearts flow, Blood comes into the right atrium from the body, moves into the right ventricle and is pushed into the pulmonary arteries in the lungs. After picking up oxygen, the blood travels back to the heart through the pulmonary veins into the left atrium, to the left ventricle and out to the body's tissues through the aorta.
Plus de 30 millions de storyboards créés

