Brooke Lowe First Red Scare Storyboard
Süžeeskeem Tekst
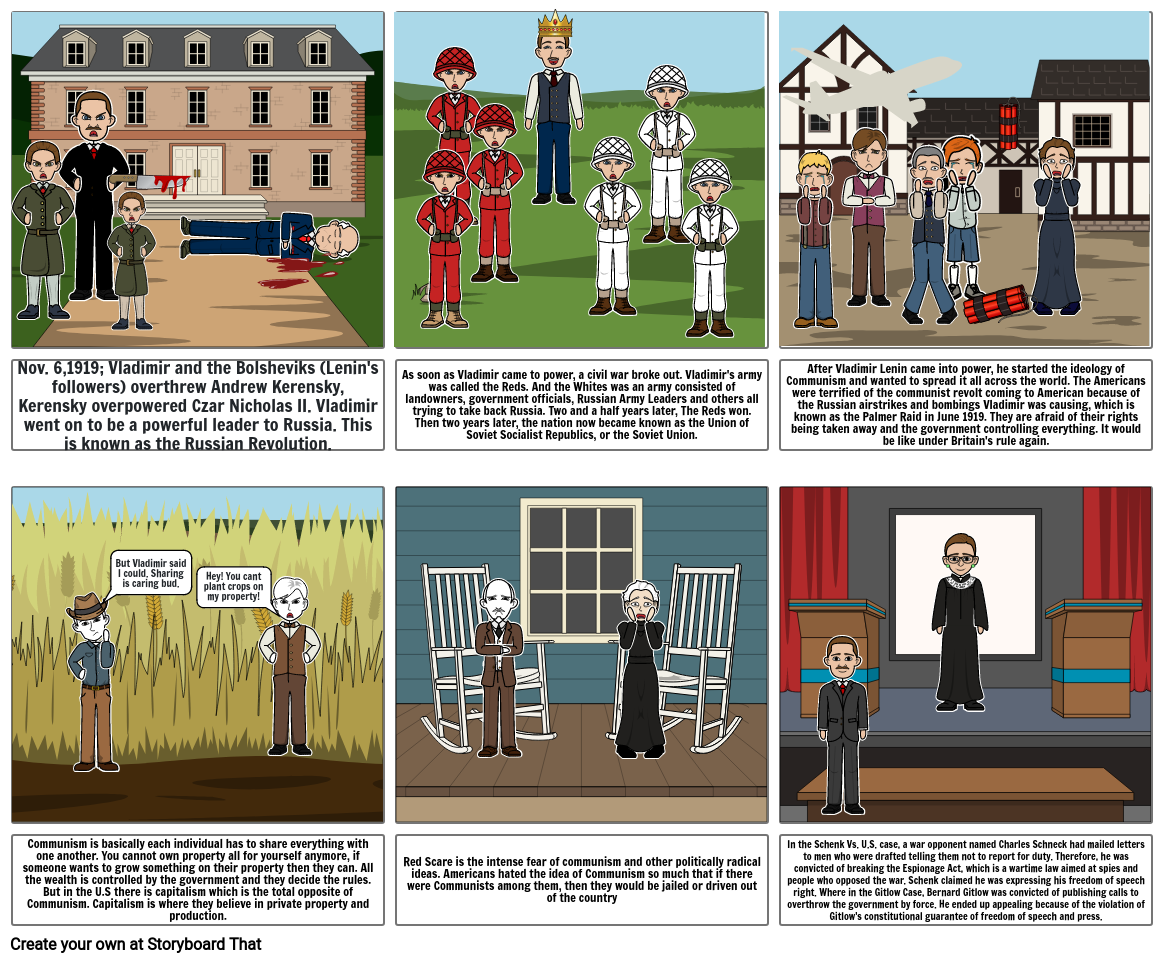
- Nov. 6,1919; Vladimir and the Bolsheviks (Lenin's followers) overthrew Andrew Kerensky, Kerensky overpowered Czar Nicholas II. Vladimir went on to be a powerful leader to Russia. This is known as the Russian Revolution.
- But Vladimir said I could. Sharing is caring bud.
- Hey! You cant plant crops on my property!
- As soon as Vladimir came to power, a civil war broke out. Vladimir's army was called the Reds. And the Whites was an army consisted of landowners, government officials, Russian Army Leaders and others all trying to take back Russia. Two and a half years later, The Reds won. Then two years later, the nation now became known as the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, or the Soviet Union.
- After Vladimir Lenin came into power, he started the ideology of Communism and wanted to spread it all across the world. The Americans were terrified of the communist revolt coming to American because of the Russian airstrikes and bombings Vladimir was causing, which is known as the Palmer Raid in June 1919. They are afraid of their rights being taken away and the government controlling everything. It would be like under Britain's rule again.
- Communism is basically each individual has to share everything with one another. You cannot own property all for yourself anymore, if someone wants to grow something on their property then they can. All the wealth is controlled by the government and they decide the rules. But in the U.S there is capitalism which is the total opposite of Communism. Capitalism is where they believe in private property and production.
- Red Scare is the intense fear of communism and other politically radical ideas. Americans hated the idea of Communism so much that if there were Communists among them, then they would be jailed or driven out of the country
- In the Schenk Vs. U.S. case, a war opponent named Charles Schneck had mailed letters to men who were drafted telling them not to report for duty. Therefore, he was convicted of breaking the Espionage Act, which is a wartime law aimed at spies and people who opposed the war. Schenk claimed he was expressing his freedom of speech right. Where in the Gitlow Case, Bernard Gitlow was convicted of publishing calls to overthrow the government by force. He ended up appealing because of the violation of Gitlow's constitutional guarantee of freedom of speech and press.
Loodud üle 30 miljoni süžeeskeemi

