stats
Süžeeskeem Tekst
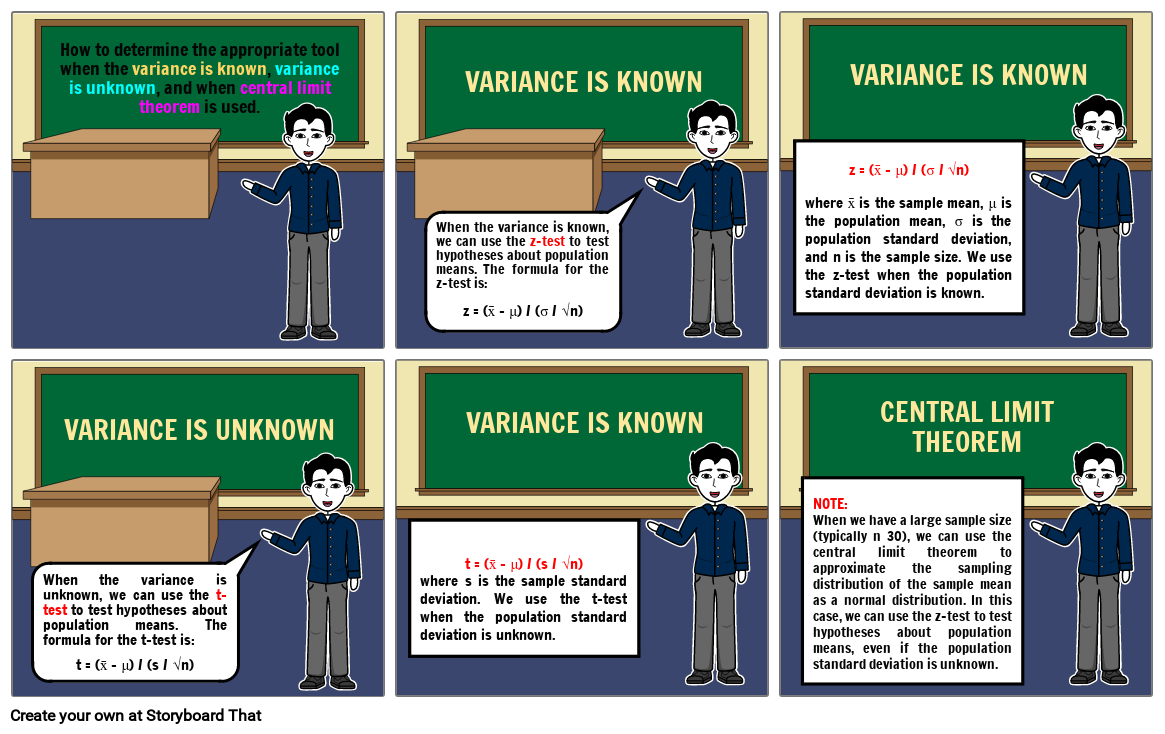
- How to determine the appropriate tool when the variance is known, variance is unknown, and when central limit theorem is used.
- When the variance is known, we can use the z-test to test hypotheses about population means. The formula for the z-test is:z = (x̄ - μ) / (σ / √n)
- VARIANCE IS KNOWN
- z = (x̄ - μ) / (σ / √n)where x̄ is the sample mean, μ is the population mean, σ is the population standard deviation, and n is the sample size. We use the z-test when the population standard deviation is known.
- VARIANCE IS KNOWN
- When the variance is unknown, we can use the t-test to test hypotheses about population means. The formula for the t-test is:t = (x̄ - μ) / (s / √n)
- VARIANCE IS UNKNOWN
- t = (x̄ - μ) / (s / √n)where s is the sample standard deviation. We use the t-test when the population standard deviation is unknown.
- VARIANCE IS KNOWN
- NOTE:When we have a large sample size (typically n 30), we can use the central limit theorem to approximate the sampling distribution of the sample mean as a normal distribution. In this case, we can use the z-test to test hypotheses about population means, even if the population standard deviation is unknown.
- CENTRAL LIMIT THEOREM
Loodud üle 30 miljoni süžeeskeemi

