COMIC STRIP ON BANKING STRUCTURE AND ITS POLICIES IN INDIA
Süžeeskeem Tekst
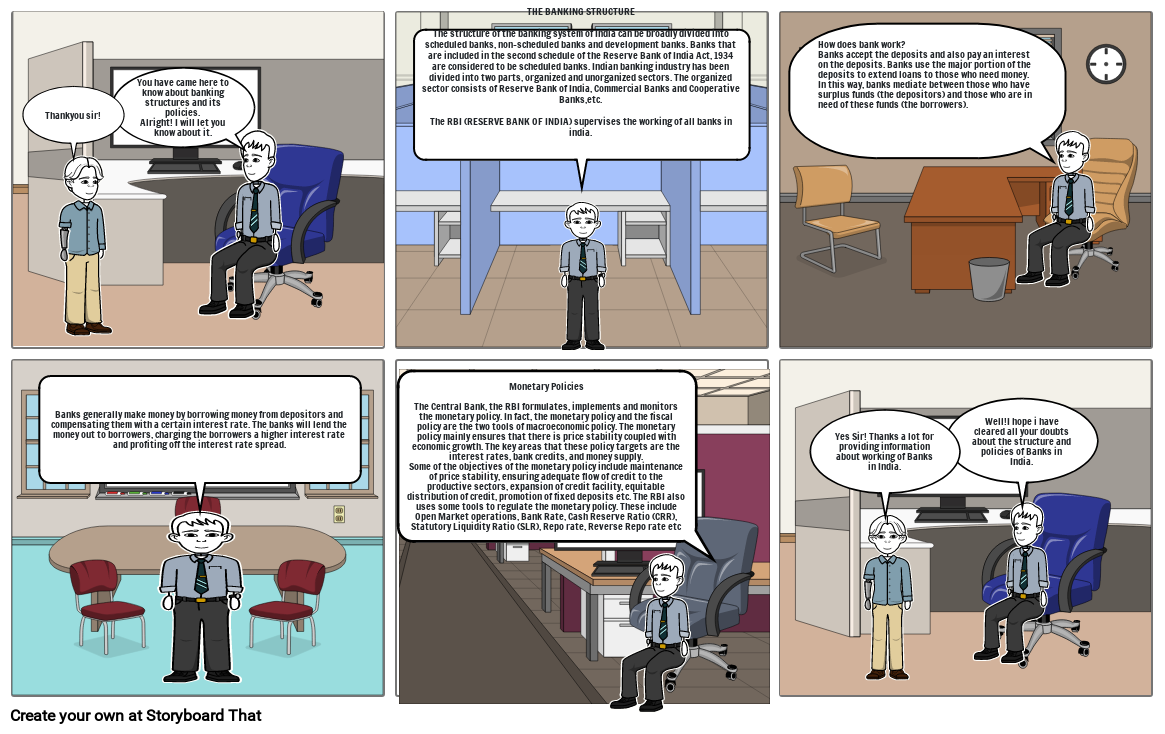
- Thankyou sir!
- You have came here to know about banking structures and its policies.Alright! I will let you know about it.
- THE BANKING STRUCTURE The structure of the banking system of India can be broadly divided into scheduled banks, non-scheduled banks and development banks. Banks that are included in the second schedule of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934 are considered to be scheduled banks. Indian banking industry has been divided into two parts, organized and unorganized sectors. The organized sector consists of Reserve Bank of India, Commercial Banks and Cooperative Banks,etc.The RBI (RESERVE BANK OF INDIA) supervises the working of all banks in india.
- How does bank work?Banks accept the deposits and also pay an interest on the deposits. Banks use the major portion of the deposits to extend loans to those who need money. In this way, banks mediate between those who have surplus funds (the depositors) and those who are in need of these funds (the borrowers).
- Banks generally make money by borrowing money from depositors and compensating them with a certain interest rate. The banks will lend the money out to borrowers, charging the borrowers a higher interest rate and profiting off the interest rate spread.
- Monetary PoliciesThe Central Bank, the RBI formulates, implements and monitors the monetary policy. In fact, the monetary policy and the fiscal policy are the two tools of macroeconomic policy. The monetary policy mainly ensures that there is price stability coupled with economic growth. The key areas that these policy targets are the interest rates, bank credits, and money supply.Some of the objectives of the monetary policy include maintenance of price stability, ensuring adequate flow of credit to the productive sectors, expansion of credit facility, equitable distribution of credit, promotion of fixed deposits etc. The RBI also uses some tools to regulate the monetary policy. These include Open Market operations, Bank Rate, Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR), Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR), Repo rate, Reverse Repo rate etc
- Yes Sir! Thanks a lot for providing information about working of Banks in India.
- Well!I hope i have cleared all your doubts about the structure and policies of Banks in India.
Loodud üle 30 miljoni süžeeskeemi

