Unknown Story
Süžeeskeem Tekst
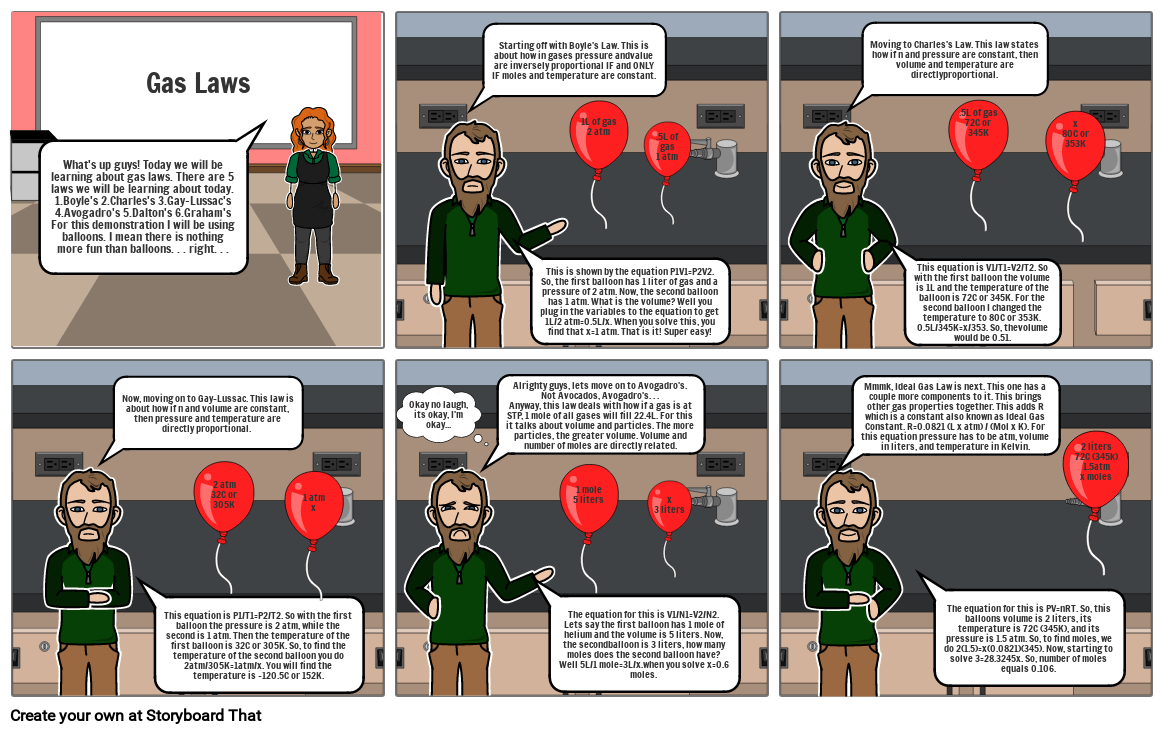
- What's up guys! Today we will be learning about gas laws. There are 5 laws we will be learning about today. 1.Boyle's 2.Charles's 3.Gay-Lussac's 4.Avogadro's 5.Dalton's 6.Graham'sFor this demonstration I will be using balloons. I mean there is nothing more fun than balloons. . . right. . .
- Gas Laws
- Starting off with Boyle's Law. This is about how in gases pressure andvalue are inversely proportional IF and ONLY IF moles and temperature are constant.
- This is shown by the equation P1V1=P2V2. So, the first balloon has 1 liter of gas and a pressure of 2 atm. Now, the second balloon has 1 atm. What is the volume? Well you plug in the variables to the equation to get 1L/2 atm=0.5L/x. When you solve this, you find that x=1 atm. That is it! Super easy!
- 1L of gas2 atm
- .5L of gas1 atm
- Moving to Charles's Law. This law states how if n and pressure are constant, then volume and temperature are directlyproportional.
- This equation is V1/T1=V2/T2. So with the first balloon the volume is 1L and the temperature of the balloon is 72C or 345K. For the second balloon I changed the temperature to 80C or 353K. 0.5L/345K=x/353. So, thevolume would be 0.51.
- .5L of gas72C or 345K
- x80C or 353K
- Now, moving on to Gay-Lussac. This law is about how if n and volume are constant, then pressure and temperature are directly proportional.
- This equation is P1/T1=P2/T2. So with the first balloon the pressure is 2 atm, while the second is 1 atm. Then the temperature of the first balloon is 32C or 305K. So, to find the temperature of the second balloon you do 2atm/305K=1atm/x. You will find the temperature is -120.5C or 152K.
- 2 atm32C or 305K
- 1 atmx
- Okay no laugh, its okay, I'm okay...
- Alrighty guys, lets move on to Avogadro's. Not Avocados, Avogadro's. . . Anyway, this law deals with how if a gas is at STP, 1 mole of all gases will fill 22.4L. For this it talks about volume and particles. The more particles, the greater volume. Volume and number of moles are directly related.
- The equation for this is V1/N1=V2/N2. Lets say the first balloon has 1 mole of helium and the volume is 5 liters. Now, the secondballoon is 3 liters, how many moles does the second balloon have? Well 5L/1 mole=3L/x.when you solve x=0.6 moles.
- 1 mole5 liters
- x3 liters
- Mmmk, Ideal Gas Law is next. This one has a couple more components to it. This brings other gas properties together. This adds R which is a constant also known as Ideal Gas Constant. R=0.0821 (L x atm) / (Mol x K). For this equation pressure has to be atm, volume in liters, and temperature in Kelvin.
- The equation for this is PV=nRT. So, this balloons volume is 2 liters, its temperature is 72C (345K), and its pressure is 1.5 atm. So, to find moles, we do 2(1.5)=x(0.0821)(345). Now, starting to solve 3=28.3245x. So, number of moles equals 0.106.
- 2 liters72C (345k)1.5atmx moles
Loodud üle 30 miljoni süžeeskeemi

