The Central Dogma Comic Strip Assignment
Texto del Guión Gráfico
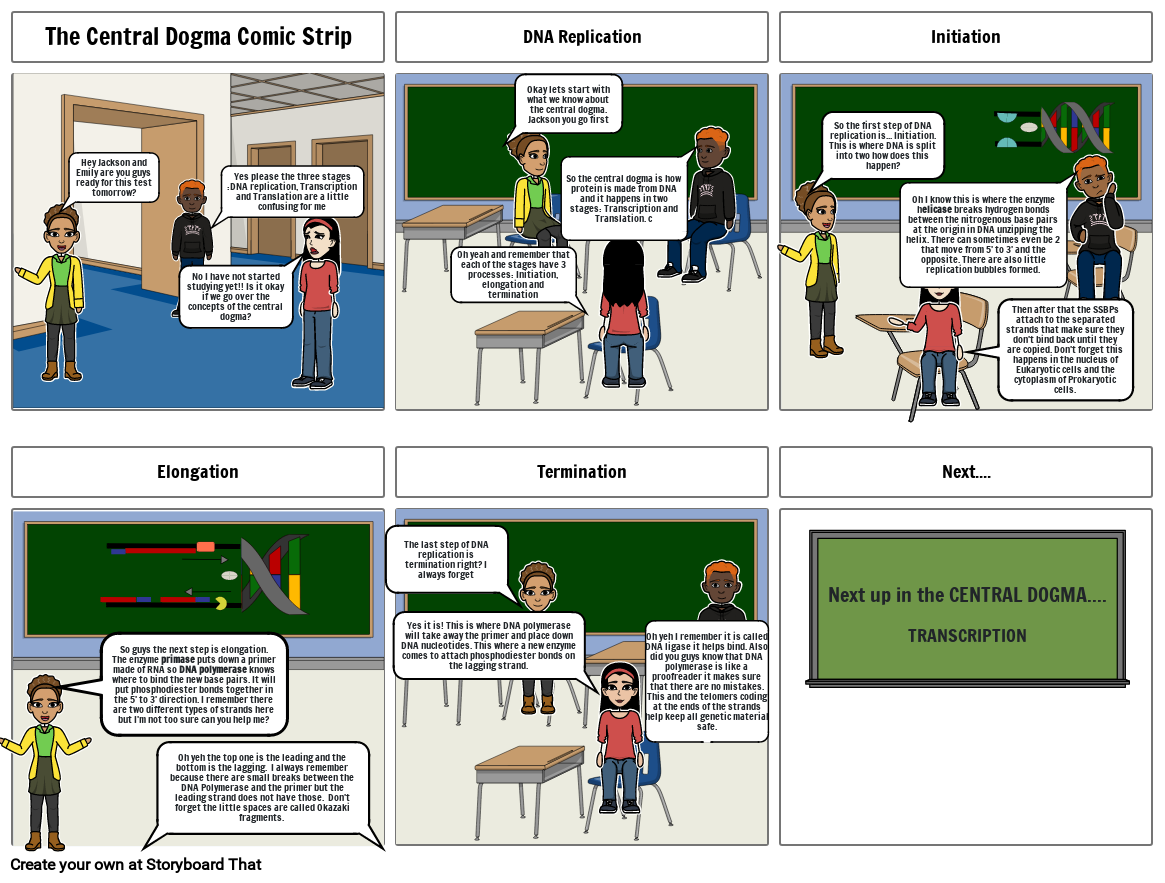
- The Central Dogma Comic Strip
- Hey Jackson and Emily are you guys ready for this test tomorrow?
- No I have not started studying yet!! Is it okay if we go over the concepts of the central dogma?
- Yes please the three stages :DNA replication, Transcription and Translation are a little confusing for me
- DNA Replication
- Oh yeah and remember that each of the stages have 3 processes: Initiation, elongation and termination
- Okay lets start with what we know about the central dogma. Jackson you go first
- So the central dogma is how protein is made from DNA and it happens in two stages: Transcription and Translation. c
- Initiation
- So the first step of DNA replication is... Initiation. This is where DNA is split into two how does this happen?
- Oh I know this is where the enzyme helicase breaks hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous base pairs at the origin in DNA unzipping the helix. There can sometimes even be 2 that move from 5' to 3' and the opposite. There are also little replication bubbles formed.
- Then after that the SSBPs attach to the separated strands that make sure they don't bind back until they are copied. Don't forget this happens in the nucleus of Eukaryotic cells and the cytoplasm of Prokaryotic cells.
- Elongation
- So guys the next step is elongation. The enzyme primase puts down a primer made of RNA so DNA polymerase knows where to bind the new base pairs. It will put phosphodiester bonds together in the 5' to 3' direction. I remember there are two different types of strands here but I'm not too sure can you help me?
- The last step of DNA replication is termination right? I always forget
- Yes it is! This is where DNA polymerase will take away the primer and place down DNA nucleotides. This where a new enzyme comes to attach phosphodiester bonds on the lagging strand.
- Termination
- Oh yeh I remember it is called DNA ligase it helps bind. Also did you guys know that DNA polymerase is like a proofreader it makes sure that there are no mistakes. This and the telomers coding at the ends of the strands help keep all genetic material safe.
- Next....
- Next up in the CENTRAL DOGMA....TRANSCRIPTION
- Oh yeh the top one is the leading and the bottom is the lagging.  I always remember because there are small breaks between the DNA Polymerase and the primer but the leading strand does not have those.  Don't forget the little spaces are called Okazaki fragments. 
Más de 30 millones de guiones gráficos creados

