Unknown Story
Storyboard Text
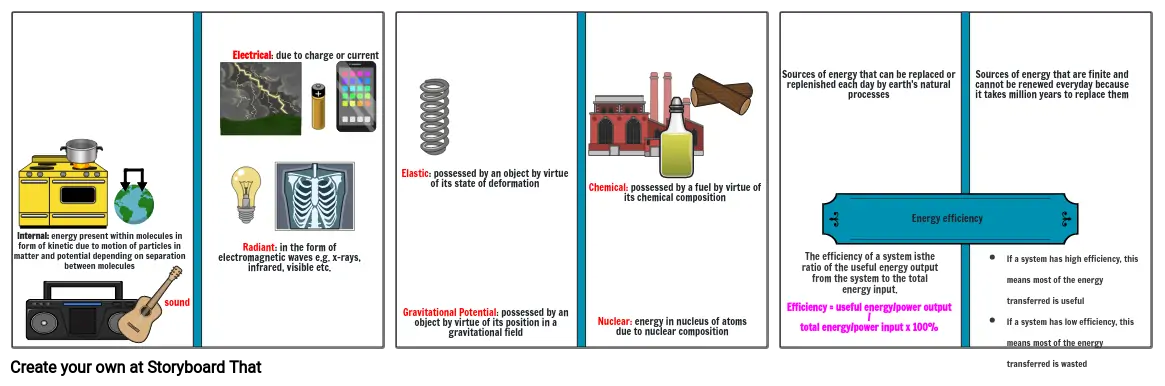
- Internal: energy present within molecules in form of kinetic due to motion of particles in matter and potential depending on separation between molecules
- sound
- Radiant: in the form of electromagnetic waves e.g. x-rays, infrared, visible etc.
- Electrical: due to charge or current
- Gravitational Potential: possessed by an object by virtue of its position in a gravitational field
- Elastic: possessed by an object by virtue of its state of deformation
- Chemical: possessed by a fuel by virtue of its chemical composition
- Nuclear: energy in nucleus of atoms due to nuclear composition
- Sources of energy that can be replaced or replenished each day by earth's natural processes
- Efficiency = useful energy/power output / total energy/power input x 100%
- The efficiency of a system isthe ratio of the useful energy output from the system to the total energy input.
- Energy efficiency
- If a system has high efficiency, this means most of the energy transferred is usefulIf a system has low efficiency, this means most of the energy transferred is wasted
- Sources of energy that are finite and cannot be renewed everyday because it takes million years to replace them
Vytvořeno více než 30 milionů Storyboardů

