plessy v ferguson
القصة المصورة الوصف
history civics
نص القصة المصورة
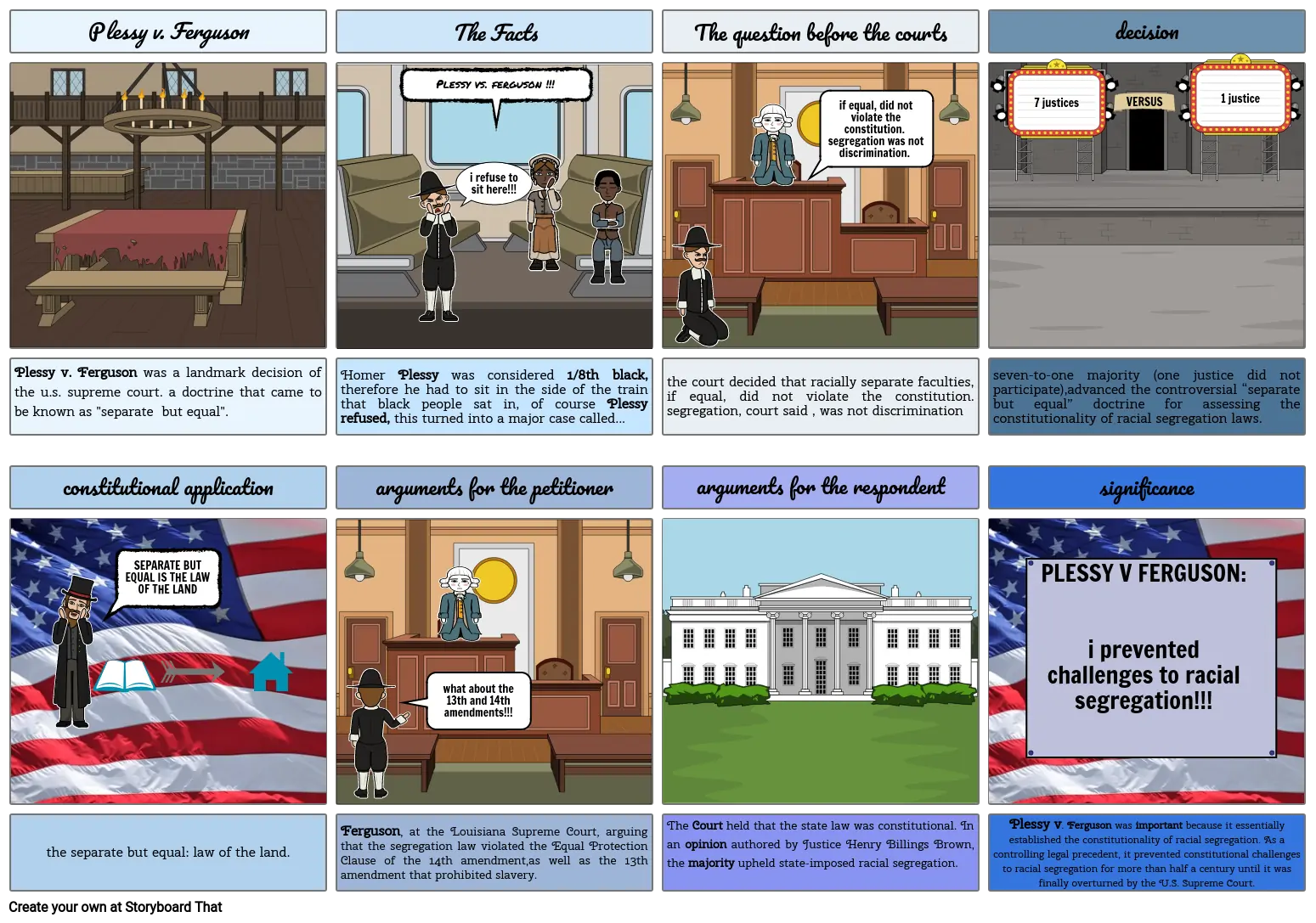
- Plessy v. Ferguson
- The Facts
- Plessy vs. ferguson !!!
- i refuse to sit here!!!
- The question before the courts
- if equal, did not violate the constitution. segregation was not discrimination.
- decision
- 7 justices
- VERSUS
- 1 justice
- Plessy v. Ferguson was a landmark decision of the u.s. supreme court. a doctrine that came to be known as "separate but equal".
- constitutional application
- SEPARATE BUT EQUAL IS THE LAW OF THE LAND
- Homer Plessy was considered 1/8th black, therefore he had to sit in the side of the train that black people sat in, of course Plessy refused, this turned into a major case called...
- arguments for the petitioner
- the court decided that racially separate faculties, if equal, did not violate the constitution. segregation, court said , was not discrimination
- arguments for the respondent
- seven-to-one majority (one justice did not participate),advanced the controversial “separate but equal” doctrine for assessing the constitutionality of racial segregation laws.
- significance
- PLESSY V FERGUSON:i prevented challenges to racial segregation!!!
- the separate but equal: law of the land.
- Ferguson, at the Louisiana Supreme Court, arguing that the segregation law violated the Equal Protection Clause of the 14th amendment,as well as the 13th amendment that prohibited slavery.
- what about the 13th and 14th amendments!!!
- The Court held that the state law was constitutional. In an opinion authored by Justice Henry Billings Brown, the majority upheld state-imposed racial segregation.
- Plessy v. Ferguson was important because it essentially established the constitutionality of racial segregation. As a controlling legal precedent, it prevented constitutional challenges to racial segregation for more than half a century until it was finally overturned by the U.S. Supreme Court.
تم إنشاء أكثر من 30 مليون من القصص المصورة

